Fig. 7.
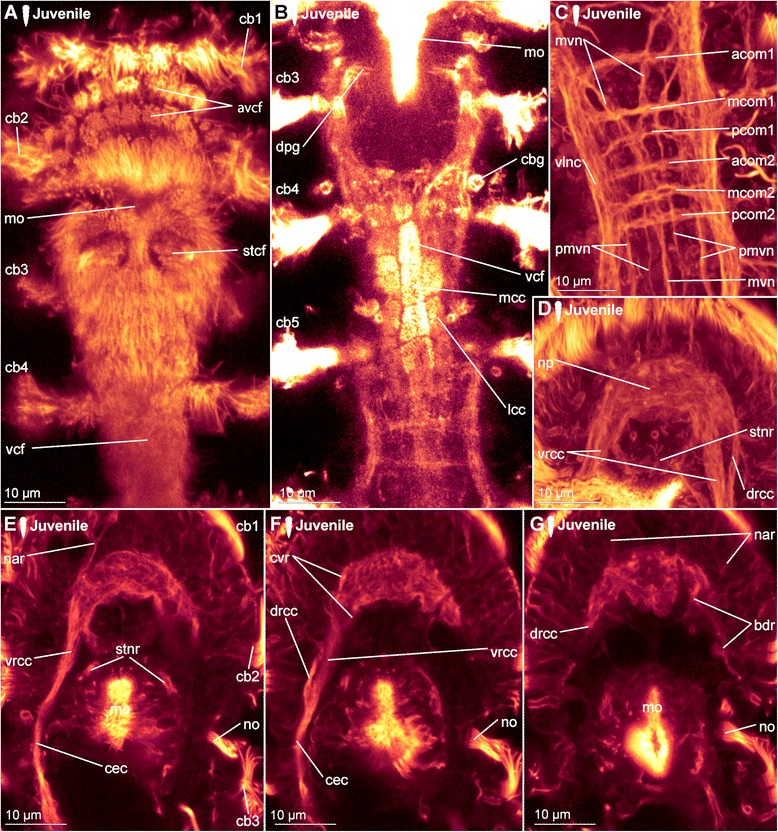
Correlation between outer ciliary and nervous structures in early juvenile females of Dinophilus gyrociliatus and details of the neuropil. Acetylated α-tubulin-like immunoreactive filaments shown in”glow”, animals are oriented with the anterior end up. a Ventral ciliary field of a juvenile female with spot-like multiciliated cells (svcf), stomatogastric ciliary fields (stcf) and more elongated multicilited cells (lcc), b multiciliated cells along the ventral body side, c detail of the anterior region of the ventral nervous system with the commissural sets, d detail of the neuopil with the dorsal and ventral root of the circumesophageal connective, e-g sections through the neuropil from the ventral to the dorsal side, showing the commissures of the ventral and dorsal root: e section through the ventral root with the base of the circumesophageal connective, f condensed fibres within the ventral root of the circumesophageal connective, g section through the dorsal root. Abbreviations: acom – anterior commissure, avcf – anteroventral ciliary field, bdr – branches of the dorsal root, cb – ciliary band, cbg – ciliary band gland, cec – circumesophageal connective, cvr – commissures of the ventral root of the circumesophageal connective, dpg – ducts of the pharyngeal glands, drcc – dorsal root of the circumesophageal connective, lcc – lateral multiciliated cell of the ventral ciliary field, mcc – median multiciliated cell of the ventral ciliary field, mcom – median commissure, mo – mouth opening, mvn – medioventral nerve, nar – nerves innervating the anterior rim, pcom – posterior commissure, pmvn – paramedioventral ventral nerve, stcf – stomatogastric ciliary field, stnr – stomatogastric nerve ring, svcf – stomatogastric ventral ciliary field, vcf – ventral ciliary field, vlnc – ventrolateral nerve cord, vrcc – ventral root of the circumesophageal connective
