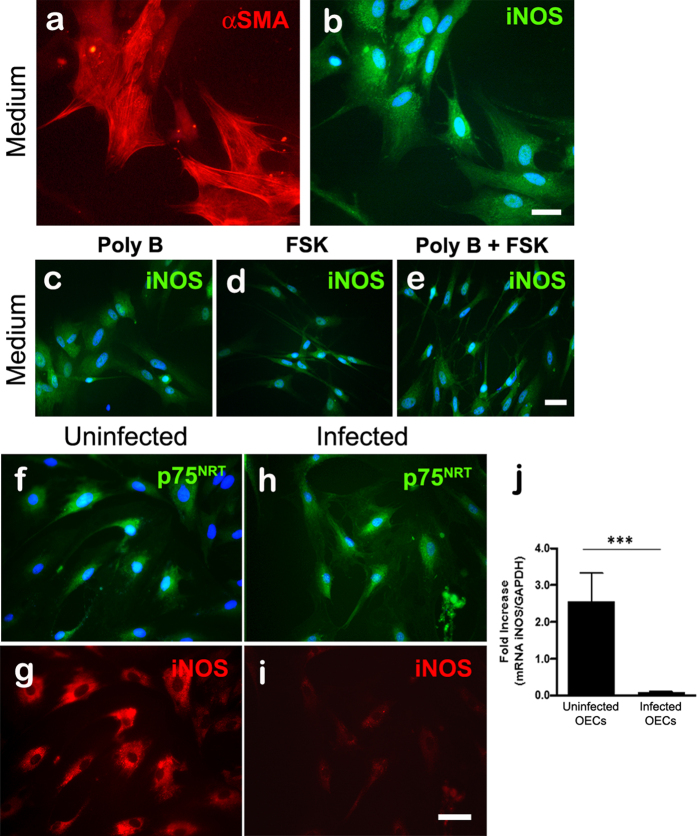
Figure 5. In vitro regulation of iNOS expression during infection of OECs by Streptococcus pneumoniae.
(a,b) OECs phenotypically identified by αSMA expressed iNOS constitutively in vitro. (c) Polymyxin B (poly B) was used as an inhibitor of LPS contamination, and the treatment of OEC cultures did not induce significant differences in the expression of iNOS. Forskolin (FSK) was added to the defined media as culture requirements for OEC cultures, and is also described as a costimulatory agent of the LPS-induced iNOS expression. (d,e) FSK alone or in combination with poly B had little or no effect on iNOS expression. S. pneumoniae infection of OECs, phenotypically identified by their expression of P75NRT, reduced the expression of iNOS (h,i) compared to uninfected cultures (f,g). The nuclei of the cells were stained with DAPI. (j) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of iNOS mRNA in uninfected and infected OEC cultures with S. pneumoniae. The graph shows a significant reduction of mRNA levels of iNOS in infected cultures compared to uninfected control OEC cultures. The s.d. values are shown, n = 4; stars indicate significance in two-tailed Student’s t-test; ***P < 0.001. All experiments were run in triplicate or quadruplicate, and each experiment was repeated two or three times. Scale bar = 25 μm (a,b); 45 μm (c–e); 30 μm (f–i).