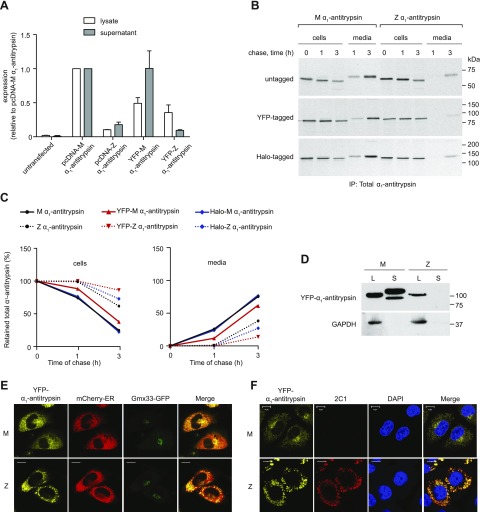
Figure 1.
Characterization of YFP-α1-antitrypsin. A) CHO cells were transfected with untagged (pcDNA) or YFP-tagged M-α1-antitrypsin or Z-α1-antitrypsin. Whole-cell lysates and supernatants were analyzed for total α1-antitrypsin production by sandwich ELISA (n = 3). B) CHO cells expressing untagged α1-antitrypsin, YFP-α1-antitrypsin, or HaloTag-α1-antitrypsin were pulse labeled with [35S]-Met/Cys for 15 min and chased for 0 to 3 h. Alpha-1-antitrypsin from Triton X-100 cell lysates and medium was immunoprecipitated with polyclonal antibody; samples were then resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and detected by autoradiography. C) Quantification of retained (left) and secreted (right) α1-antitrypsin reveal comparable profiles of untagged and tagged protein. D) Western blot of cell lysates (L) and medium supernatants (S) from YFP-α1-antitrypsin CHOs show band of expected size for YFP-α1-antitrypsin fusion protein. Lower-mobility mature glycoform of α1-antitrypsin is visible only in YFP-M-α1-antitrypsin-conditioned medium. E) CHO cells cotransfected with YFP-α1-antitrypsin (yellow), mCherry-ER (red), and Golgi marker Gmx33-GFP (green). YFP-M-α1-antitrypsin colocalized with both ER and Golgi markers, whereas YFP-Z-α1-antitrypsin accumulated in punctate inclusions labeled with ER marker and failed to colocalize with Golgi marker. Scale bars, 10 µm. F) CHO cells were transiently transfected with YFP-α1-antitrypsin, fixed, labeled with 2C1 antibody, and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy. Positive 2C1 staining indicative of pathogenic polymer formation was observed only in cells expressing YFP-Z-α1-antitrypsin. Scale bars, 10 µm.