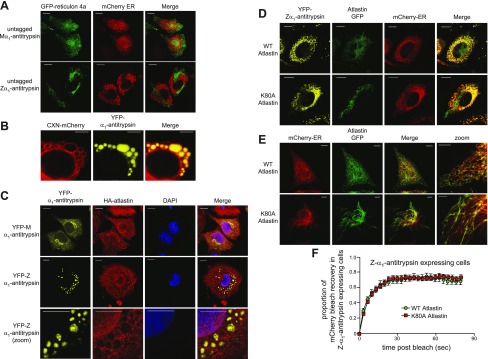
Figure 7.
Transport between inclusions is insensitive to dominant negative atlastin. A) Lack of colocalization of GFP–reticulon 4a and mCherry-ER: CHO cells were cotransfected with untagged M- or Z-α1-antitrypsin, GFP–reticulon 4a (green) and mCherry-ER (red). Reticular pattern is evident of GFP–reticulon 4a and mCherry-ER in M-α1-antitrypsin-expressing cells, in contrast to lack of colocalization between tubular GFP–reticulon 4a and punctate mCherry-ER in Z-α1-antitrypsin-expressing cells. Scale bars, 10 µm. B) Integral membrane protein CNX-mCherry decorates membranes of Z-α1-antitrypsin-containing inclusions. Scale bars, 5 µm. C) Lack of colocalization of atlastin and YFP-tagged α1-antitrypsin: cells were cotransfected with either YFP-M-α1-antitrypsin or YFP-Z-α1-antitrypsin (yellow) and hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged atlastin, then stained with anti-HA antibody (red). Scale bars, 10 µm. D) Lack of colocalization of atlastin-GFP- and YFP-tagged α1-antitrypsin: coexpression of GFP-tagged wild-type and K80A mutant atlastin (green), YFP-Z-α1-antitrypsin (yellow), and mCherry-ER (red). Poor localization is evident between atlastin-GFP and Z-α1-antitrypsin. Scale bars, 10 µm. E) Coexpression of GFP-tagged wild-type and K80A mutant atlastin (green) with mCherry-ER (red). Evident is tubular, nonbranching nature of ER in cells expressing mutant atlastin. F) mCherry FRAP was performed in CHO cells coexpressing mCherry-ER, Z-α1-antitrypsin, and either wild-type or K80A mutant atlastin.