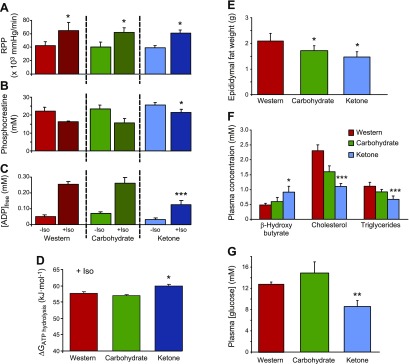
Figure 3.
Effect of feeding the ketone diet for 66 d on myocardial contractile function and high-energy phosphate levels, epididymal fat pad weights, and plasma metabolite concentrations. A) RPP, a measure of workload, was increased by 34% using an infusion of 10 nM isoproterenol (Iso) for 5 min in each rat heart. *P < 0.05 vs. –Iso. B) PCr remained higher in ketone-fed rat hearts during the increased workload compared with hearts from rats that were fed either of the other 2 diets. *P < 0.05 vs. rats fed the Western and carbohydrate diets. C) Free ADP concentration was lower in ketone-fed rat hearts during the increased workload compared with hearts from rats that were fed either of the other 2 diets. ***P < 0.001 vs. rats fed the Western and carbohydrate diets. D) Free energy of ATP hydrolysis was higher in hearts from ketone-fed rats during the high workload. *P < 0.05 vs. rats fed the Western and carbohydrate diets. E) Epididymal fat pad weights were lower in rats that were fed the ketone and carbohydrate diets. *P < 0.05. F) Ketone diet increased plasma concentrations of d-β-hydroxybutyrate and lowered plasma cholesterol and triglycerides. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 vs. rats fed the Western diet. G) Ketone diet lowered plasma glucose concentrations. **P < 0.01, vs. rats fed the Western diet.