Figure 1.
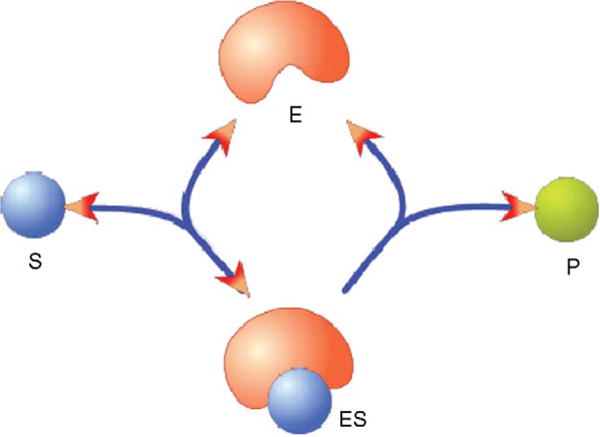
Enzyme-catalyzed reaction. The enzyme, E, converts the substrate, S, to the product, P. The enzyme and substrate form an intermediate complex, ES, which can dissociate back to E and S or form P and free the enzyme, E. This model treats the production of P from the ES complex as an irreversible reaction because the reversible reaction rate may be negligible.
