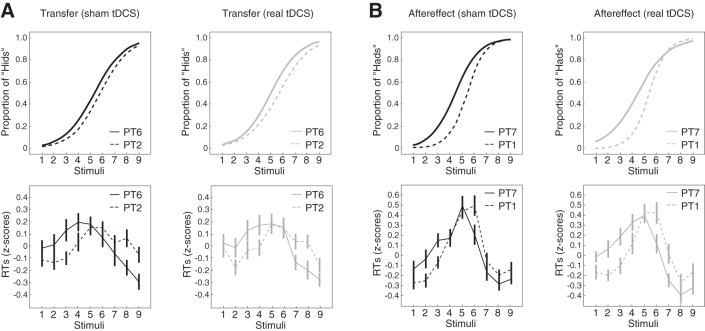
Fig. 3.
Training altered speech perception. A: top, psychometric functions were fit to the proportion of hid responses before (PT2, broken lines) and after (PT6, solid lines) perceptual training. Prior training on the head-to-had continuum altered the proportion of hid responses on the head-to-hid continuum such that participants were more likely to report hearing hid. Bottom, log-normalized reaction times were computed and displayed as z-scores for each stimulus before (PT2, broken lines) and after (PT6, solid lines) perceptual training. Changes in the perceptual boundary were mirrored by changes in reaction times to some of the stimuli. B: top, psychometric functions were fit to the proportion of had responses before (PT1, broken lines) and after (PT7, solid lines) perceptual training. Following training, participants were more likely to report hearing had. Bottom, log-normalized reaction times were computed and displayed as z-scores for each stimulus before (PT1, broken lines) and after (PT7, solid lines) perceptual training. Changes in the psychometric function were mirrored by changes in reaction times. Error bars represent ± SE.