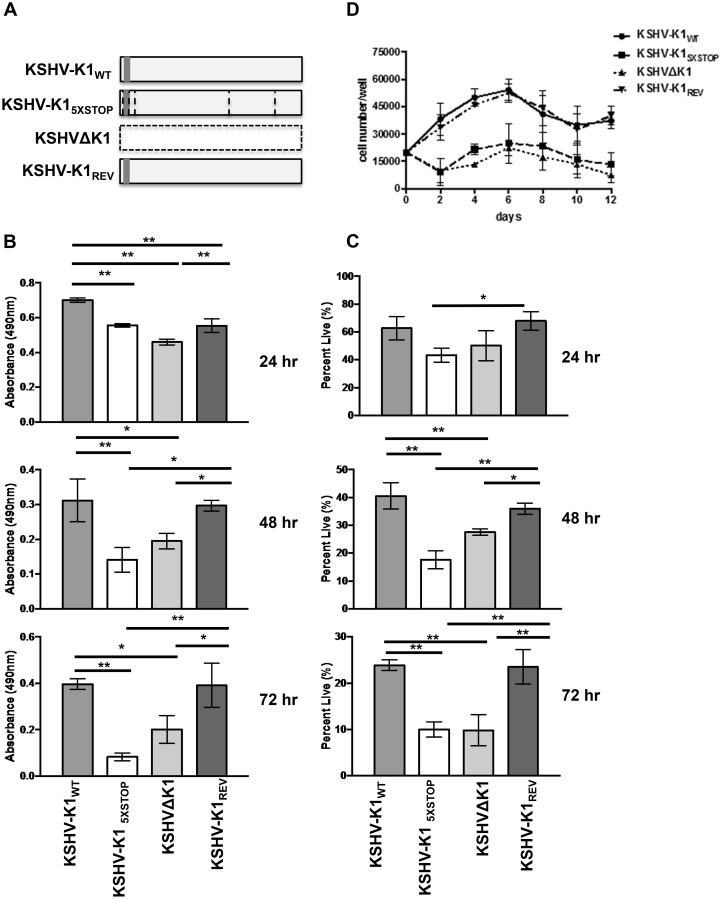
Fig 1. KSHV K1 mutant infected cells exhibit decreased survival following nutrient deprivation.
(A) KSHV-K1WT and KSHV-K1REV (revertant) harbor a wild type K1 gene. The KSHV-K15XSTOP has a K1 mutant gene that contains 5 stop codons. Three of the stop codons follow the first start codon of the K1 gene. The other two stop codons replace two downstream ATG codons at positions 481 and 763 in the K1 gene. The KSHVΔK1 mutant has had the K1 gene replaced by a RpsL-Neo cassette. Hence, the KSHV-K15XSTOP and KSHVΔK1 are not able to express any portion of the K1 protein. The grey box represents FLAG and horizontal lines represent the stop codons in KSHV-K15XSTOP. HUVEC infected with KSHV-K1WT, KSHV-K15XSTOP, KSHVΔK1 or KSHV-K1REV were starved of serum and growth factors for 24, 48 and 72 hours. (B) The proportion of metabolically active cells within each group was determined using an MTS assay. Error bars are the standard deviation of biological triplicates. GraphPad Prism was used to determine one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-test. *P<0.05, **P<0.005 (C) The percent of viable cells/well for each group was determined by trypan blue exclusion assay. Percent was calculated by normalization to total number of cells plated. Error bars are the standard deviation of biological triplicates. (D) KSHV-K1WT, KSHV-K15XSTOP, KSHVΔK1, and KSHV-K1REV infected iSLK cells were cultured without serum. Cell viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion. Error bars are the standard deviation of biological triplicates.