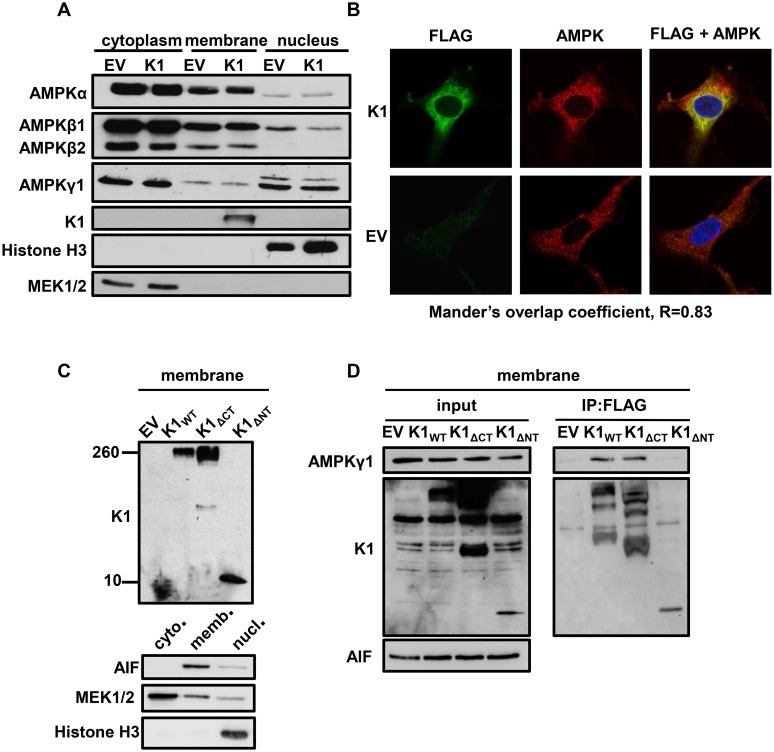
Fig 6. K1 and AMPK associate in membranes in the perinuclear area of the cell.
(A) HEK-293 cells stably expressing empty vector (EV) or FLAG-K1 (K1) were lysed and fractionated into cytoplasmic, membrane and nuclear fractions. Immunoblots were probed for endogenous AMPK subunit and isoforms. (B) HUVEC stably expressing empty (EV) or FLAG-K1 (K1) were fixed and permeabilized. Cells were then stained with anti-FLAG directly conjugated to FITC antibody, and an AMPKβ1/2 antibody, followed by an anti-rabbit conjugated to Alexa Fluor 647. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Stained HUVEC were evaluated with a Zeiss 700 confocal microscope using a 63X oil objective. Mander’s overlap coefficient (R = 0.83) was generated using ImageJ. (C) HEK-293 cells were transiently transfected with EV (pcDNA3), K1WT, K1ΔCT and K1ΔNT. Cell lysates were separated into membrane, cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. We evaluated the membrane fraction for expression of the K1 domain deleted mutants by immunoblot. We also immunoblotted for AIF (membrane), MEK1/2 (cytoplasm) and Histone H3 (nucleus). (D) HEK-293 cells were transiently transfected with the constructs described in (C) with the addition of AMPKγ1. Cell lysates were separated into membrane, cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. We immunoprecipitated FLAG K1 and immunoblotted for AMPKγ1 or FLAG using only the membrane fraction.