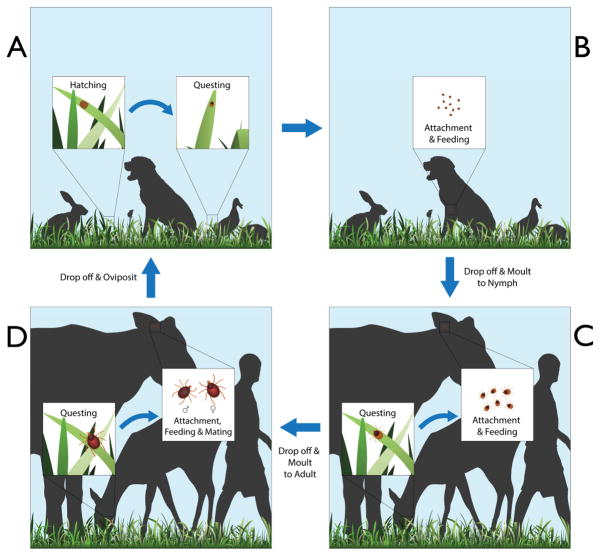
Figure 2.
Idealized life cycle of an Ixodes spp. tick with three hosts, showing the three stages (larva, nymph, and adult) (16). The eggs incubate in ground litter (A), protected against stressful environmental conditions (e.g., water losses). When the larvae hatch, they climb the vegetation, questing for a host (A→B). Larvae feed on such hosts (B), and when engorged, drop off to the ground and molt to nymphs (B→C). The nymphs quest for a second host, feed, and molt again off the host (C→D). The resulting adults attach to a third host, feed, and mate, and the females drop off for ovipositing on the ground.