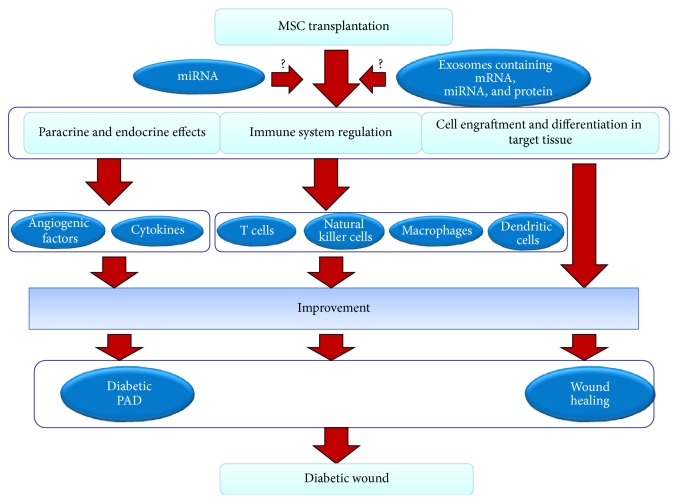
Figure 2.
Mechanism of the effect of transplantation of MSCs on diabetic wound. The mechanism of diabetic wound recovery by MSC transplantation stems from three pathways: the first is the secretion of angiogenic and factors and cytokines, the second is regulation of the immune system, and the third is the engraftment and differentiation of the cells into tissue constituents. Stem cells can specifically improve the local secretion and expression of angiogenic factors and cytokines, which contributes to the improvement of diabetic PAD and diabetes itself. Stem cells can also regulate the activities of T cells, natural killer cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells and can inhibit infections and inflammatory reactions. Moreover, MSCs can differentiate into target tissues to achieve a reparative effect. These effects may be associated with miRNA and MEX.