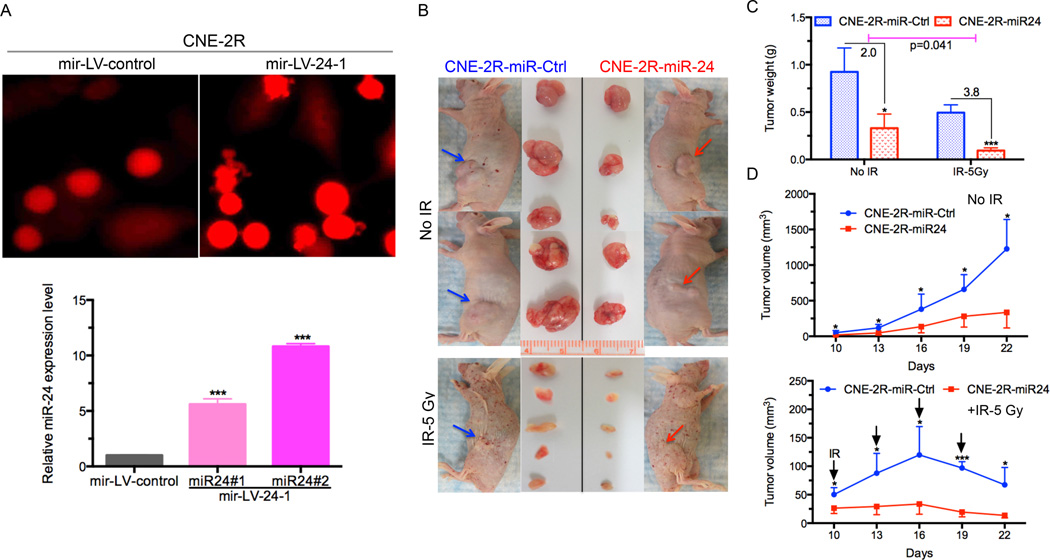
Figure 2.
MiR-24 inhibits NPC tumor growth and sensitize NPC tumor to radiation in vivo. (A) Representative photos of successful establishment of NPC stable cells (CNE-2R) overexpressing miR-24 by transducing with mir-LV-24-1 or mir-LV-control as control group (upper panel). qRT-PCR analysis of miR-24 expression level in two colonies 31 and #2 of CNE-2R cells that were transduced with a lentivirus mir-LV-24-1 for overexpressing miR-24. Results are presented as the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. Raw data were analyzed with 2−ΔΔCt. U6 snRNA was used as an internal control. ***P<0.001, Student’s t-test. (B) BALB/c athymic nu/nu mice with tumors and resected tumors are shown (n=5 per group). Red arrow: miR-24–overexpressing group injected in right flank. Blue arrow: miR-ctrl group injected in left flank. The upper panel is without IR treatment and the bottom panel is treated with IR (at a dose of 5Gy). (C) Weight of xenograft tumors is significantly reduced by miR-24 overexpressing xenografts than control, combined with IR or not. Tumors were weighed after resection. Results are expressed as the mean ± s.e.m. *, P <0.05; **, P <0.0001, Student’s t-test. (D) miR-24 expressing NPC xenografts induced tumor regression and slow the rate of tumor growth compared with miR-Control, throughout the course of the treatment. Growth curves of xenograft tumors after the injection with miR-24 overexpressing cells and mir-LV-ctrl cells combined with IR (bottom panel) or not (top panel). Tumor volume is reported as mean tumor volume ± s.d for each group of five mice. *, P <0.05; ***, P <0.0001, Student’s t-test.