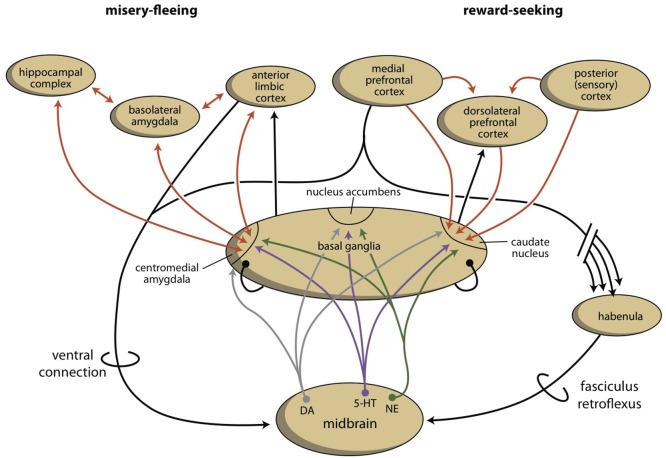
Figure 3.
The organization of the misery-fleeing and reward-seeking regulatory systems. The series of limbic and extrapyramidal basal ganglia that form converging processing units are separated from each other by the system that contains the nucleus accumbens. These units regulate motivations to exhibit misery-fleeing and reward-seeking behaviors. The activity of the basal ganglia processing unit is regulated by monoaminergic neurons from the midbrain, which are, in turn, controlled by the cerebral cortex, through a direct (ventral) and an indirect (dorsal) connection. The dorsal connection includes the habenula and the fasciculus retroflexus. [Note: the figure is slightly changed in Loonen and Ivanova, (submitted)]. Red arrows, glutamatergic; gray arrows, dopaminergic; purple arrows, serotonergic; green arrows, adrenergic; black arrows, undetermined neurochemically.