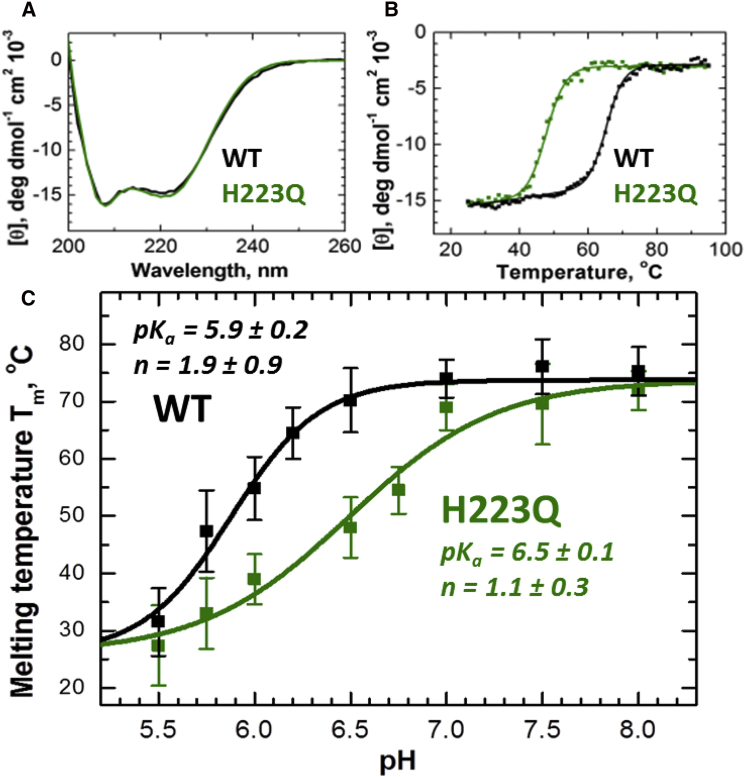
Figure 2.
CD spectroscopic comparison of the secondary structure and thermal stability of the WT (black) and H223Q (green) T domains. (A) CD spectra for the two proteins coincide at all pH values, suggesting identical secondary structure (pH 6.5 shown). (B) Thermal denaturation was followed by the changes in ellipticity measured at 222 nm at pH 6.5. Solid lines represent a fit to Eq. 1 with the following parameters: Tm = 65.2 ± 0.1°C, ΔH° = −77 ± 3 kcal/mole for WT and Tm = 47.9 ± 0.1°C, ΔH° = −73 ± 3 kcal/mole for WT. (C) pH dependence of the melting temperature, Tm, calculated from CD data such as those in (B) (average of two to three measurements shown). The data were fitted to Eq. 2 to estimate the apparent pKa and n values, presented on the graph. The WT and mutant proteins were expressed in Escherichia coli and purified as described in (44). CD measurements were in cuvettes of 1 mm path length using a Jasco-720 spectropolarimeter (Japan Spectroscopic), as described previously (55). To see this figure in color, go online.