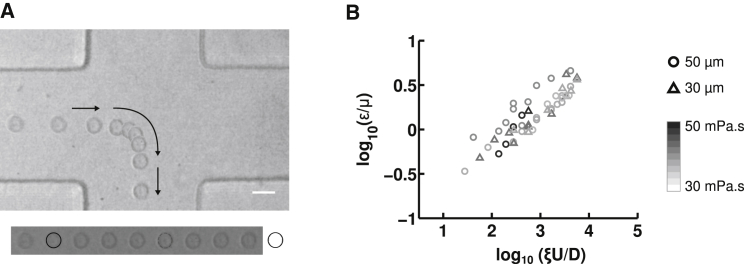
Figure 3.
Measurement of cellular viscoelastic properties. (A) Time-lapse images of a 3T3 fibroblast stretching in extensional flow as it passes through the stagnation point region. Arrows denote the direction of movement. Viscoelastic power-law constitutive model parameters are extracted from the observed deformation. Cross-slot dimensions are 100 μm wide and 30 μm deep and the strain rate is ξU/D ∼ 1690 s−1 at a 500 μL/h flow rate. The time between images is 0.5 ms, and the scale bar is 20 μm. We can observe that cell deformation increases as cells pass through the central region of the cross-slot, as is further detailed in Fig. S5. (B) Control TIC cross-slot deformation at various flow rates in devices of varying dimensions and for different suspending fluid viscosities. Each data point represents a separate experimental condition, with 10 ≤ n ≤ 30 fitted for the reported average deformation. Marker color indicates fluid viscosity, μ, using a gray scale (from white, 30 mPa·s, to black, 50 mPa·s), and the pattern indicates the cross-slot half-width, D (triangles, 35 μm; circles, 50 μm). Flow rates varied between 10 μL/h and 1000 μL/h. Height was kept constant at 30 μm.