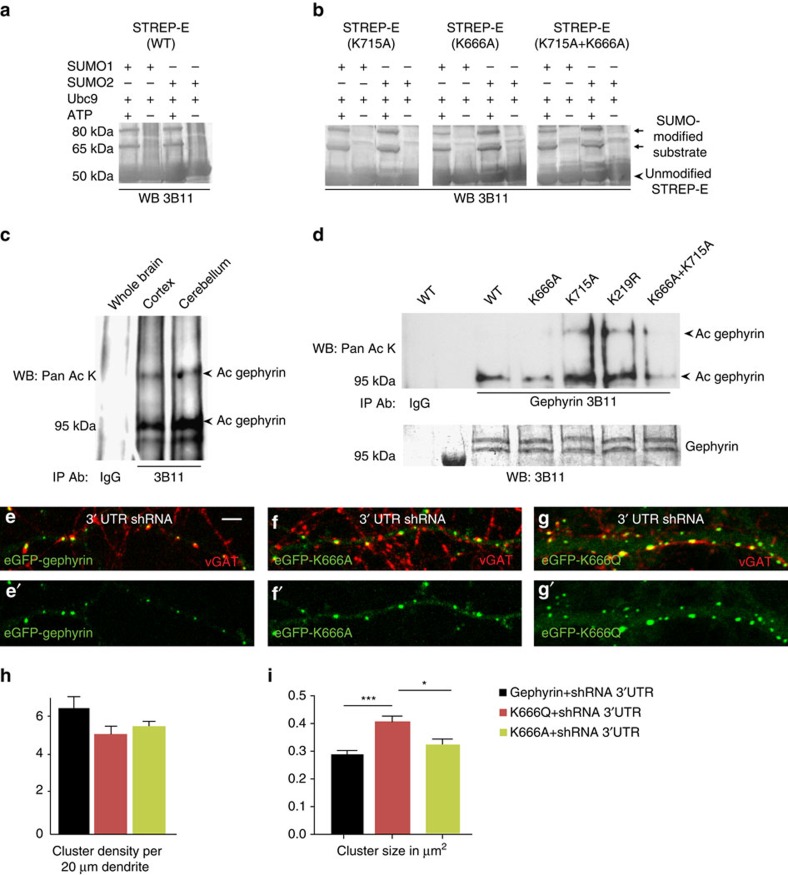
Figure 5. K666 is a novel acetylation site on gephyrin.
(a) In vitro SUMO reaction to using bacterial expressed and purified STREP-E domain shows both SUMO1 and SUMO2 conjugation at the carboxy terminus. (b) In vitro SUMO reaction using consensus site mutants K666A, K715A and K666A+K715A shows SUMOylation. (c) In vivo analysis after denaturing IP for gephyrin and WB for Pan Lys-Ac residue shows that gephyrin is acetylated in vivo. (d) Acetylation assay using FLAG–gephyrin, K666A, K715A, K219R or K666A+K715A site mutants in HEK293 cells. Denaturing IP for FLAG–gephyrin followed by WB against Pan Lys-Ac residue shows loss of acetylation in K666A and K666A+K715A mutants. Gephyrin levels after IP was determined by stripping the blot and WB using 3B11 antibody (lower panel). (e–g') Morphology of eGFP–K666A and eGFP–K666Q mutants in primary hippocampal neurons compared with WT gephyrin. (h) Synaptic cluster density show similar distribution for eGFP–K666A and eGFP–K666Q compared with eGFP–gephyrin. (i) Mean size of eGFP–gephyrin and eGFP–K666A mutant is similar, but eGFP–K666Q has a significantly higher cluster size. Scale bar, 5 μm. Images from atleast four independent experimental replicates were analysed; error bars are s.e.m.