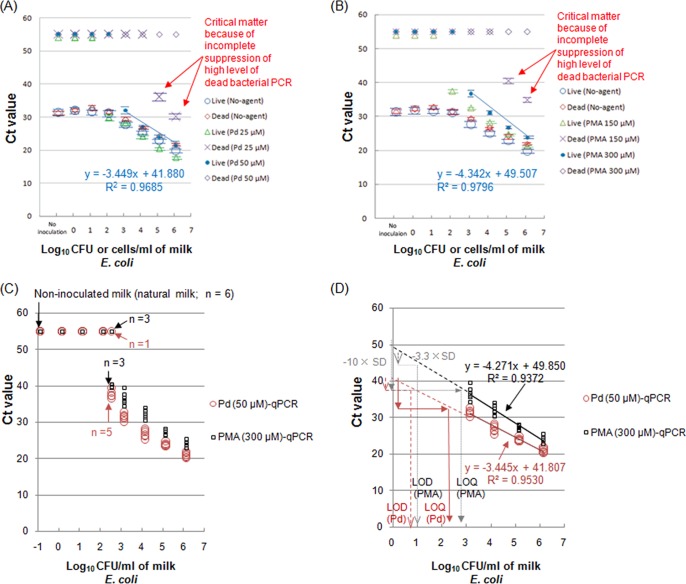
FIG 2.
Distinguishing between live and dead E. coli bacteria in pasteurized milk by qPCR following Pd compound treatment compared with the currently used PMA treatment. (A) The qPCR results for Pd compound treatment without DNA isolation (direct-qPCR): large-volume (12-ml) milk samples were exposed to 25 or 50 μM Cl2(ŋ-cycloocta-1,5-diene)Pd(II). (B) The qPCR results for PMA treatment without DNA isolation (direct-qPCR): large-volume (12-ml) milk samples were subjected to 150 or 300 μM PMA. (C) Pd-direct-qPCR and PMA-direct-qPCR using milk with artificially inoculated live E. coli and noninoculated 12-ml milk samples. Both methods were performed with 6 replicates for 8 different inoculations and for noninoculated milk (milk blank). (D) Linearity and variance for Pd-direct-qPCR and PMA-direct-qPCR using 12-ml milk samples with artificially inoculated live E. coli. Six CT value replicates for the currently used and alternative methods were plotted for four different levels of live E. coli (lower and higher levels).