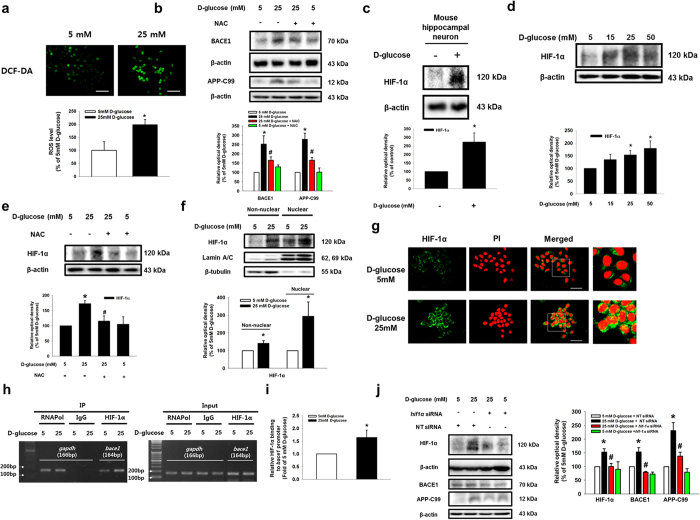
Figure 3. Role of ROS-induced HIF-1α in BACE1 expression by high glucose.
(a) DCF-DA–sensitive SK-N-MC cells were visualized by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 50 μm (magnification, ×600). Intracellular ROS generation was quantified by using luminometer. Data are presented as a mean ± S.E. of two independent sixth dishes. (b) BACE1, APP-C99 and β-actin expressions were detected by western blotting. (c) Mouse hippocampal neuron was incubated with 25 mM D-glucose for 24 h HIF-1α and β-actin expressions of mouse hippocampal neuron were detected by western blotting. Each data shown in the result is representative image of five independent experiments. (d,e) NAC (5 mM) was pretreated to cells, and then HIF-1α and β-actin expressions of SK-N-MC were detected by western blotting. (f) Non-nuclear protein and nuclear expressions were normalized by β-tubulin and lamin A/C repectively. (g) Cells were immunostained with HIF-1α and PI. Scale bars, 50 μm (magnification, ×800). (h) DNA was immunoprecipitated with RNA polymerase, IgG and HIF-1α antibodies. The immunoprecipitation and input samples were amplified with primers of gapdh and bace1 gene promoters. (i) Quantatative data was analyzed by real time PCR of two independent experiments of triple dishes. (j) SK-N-MC cells were transfected by siRNAs for 24 h prior to D-glucose treatment. HIF-1α, APP-C99, BACE1 and β-actin were detected by western blotting. Each western blot image shown is representative of three independent experiments. Data are presented as a mean ± S.E. *p < 0.05 versus 5 mM of D-glucose treatment, #p < 0.05 versus 25 mM of D-glucose treatment. All western blot data were cropped and acquired under same experimental conditions.