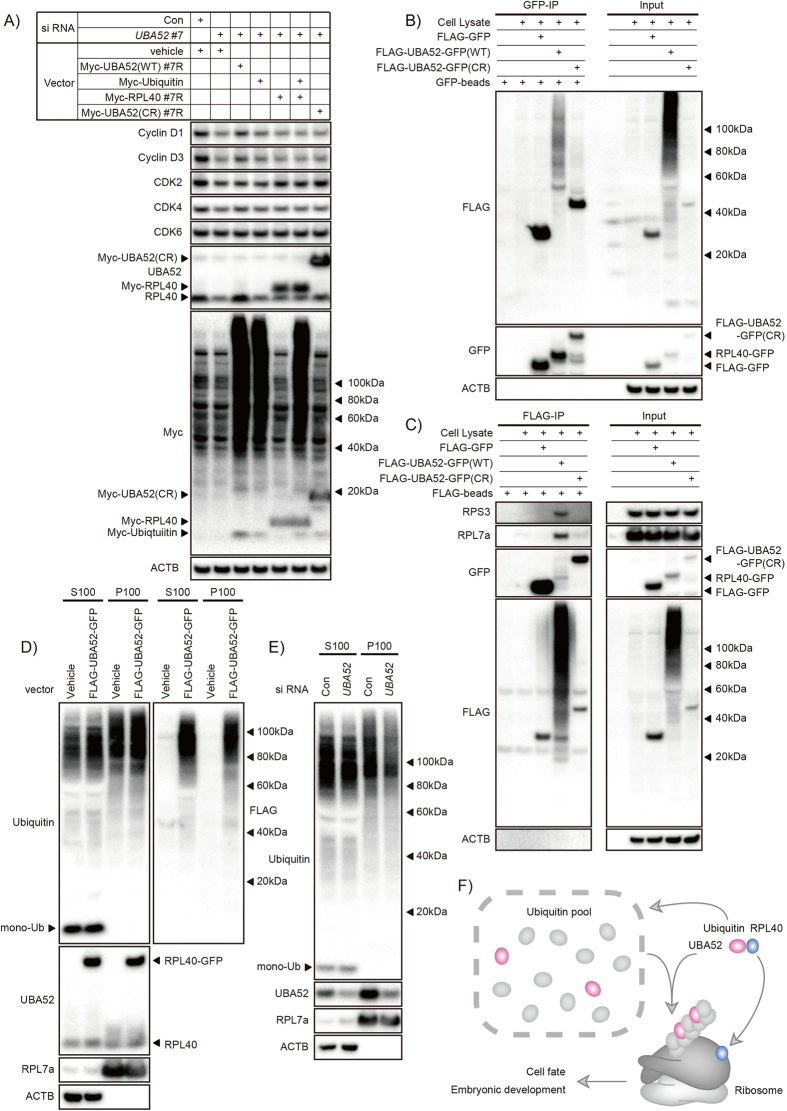
Figure 4. Ubiquitin cleaved from UBA52 forms a molecular complex with RPL40.
(A) Myc-UBA52 (WT) regulates cyclin D expression. DLD-1 cells were transfected with a UBA52 siRNA. After 6 h, DLD-1 cells were transfected with the siRNA-resistant vectors indicated. Twenty-seven hours later, cells were harvested for immunoblotting. Data are representative of more than three independent experiments. (B) RPL40 binds ubiquitinated molecules. DLD-1 cells were transfected with FLAG-UBA52-GFP (WT) and other vectors. Twenty-four hours later, cells were lysed and protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with GFP antibody and immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. Data are representative of more than three independent experiments. (C) Ubiquitin, cleaved from UBA52, forms a molecular complex with ribosome. DLD-1 cells were transfected with FLAG-UBA52-GFP (WT) and other vectors. Twenty-four hours later, cells were lysed and protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with FLAG antibody and immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (D) Subcellular fractions of FLAG-UBA52-GFP expressed DLD-1 cells. DLD-1 cells were transfected with FLAG-UBA52-GFP vector or vehicle, and 24 h later, lysed for ultracentrifugation at 10,000 × g for 1 h. S100 (cytosol) and P100 (crude ribosome pellet) fractions were immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (E) Subcellular fractions of UBA52-deficient DLD-1 cells. DLD-1 cells were transfected with UBA52 siRNA or control siRNA, and 24 h later, ultracentrifugation was performed. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (F) Schematic showing that UBA52 is a dual regulator of ribosomal function. RPL40 influences the ribosomal biogenesis as a ribosomal protein, at the same time, ubiquitin cleaved from UBA52 generates ubiquitination of the ribosomal protein complex.