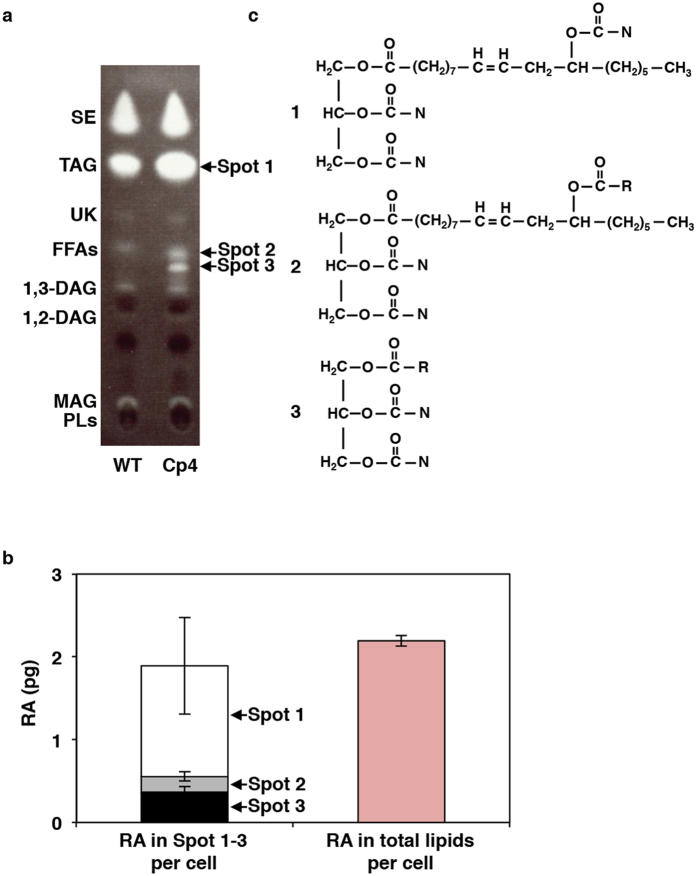
Figure 3. Three types of triacylglycerol containing ricinoleic acid were accumulated in Cp4 cells growing at 15 °C.
(a) This-layer chromatography (TLC) analysis of lipid extracts from wild-type (WT) and Cp4 lines. Three Cp4-specific spots (No. 1–3), in which ricinoleic acid (RA) was detected, are indicted by arrows. Spot positions of lipid standards (1,2-DAG, 1,2-diacylglycerol; 1,3-DAG, 1,3-diacylglycerol; FFAs, free fatty acids; MAG, monoacylglycerol; PLs, polar lipids; SE, sterol ester; TAG, triacylglycerol; UK, unknown) are shown on the left side. (b) Distribution pattern of RA in each spot (left) and total content of RA (right) in Cp4 cells on d 7. (c) Structures of three types of TAG molecules containing RA extracted from each spot in (a). 1. mono-estolide (ME) TAG, 2. 1-OH ME TAG, and 3. 1-OH TAG. These structures were identified by liquid chromatography combined with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis shown in Fig. 4 and Supplemental Figs S9–S10. N, acyl chain from endogenous normal fatty acids (mainly 14:0, 16:0, and 16:1); R, acyl chain from ricinoleic acid, WT, wild-type.