Figure 2. S. aureus actively penetrates human skin organotypic equivalents.
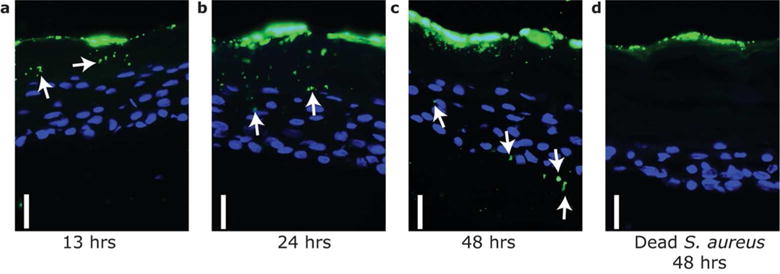
Time-dependent entry of S. aureus across the epidermis of a human skin organotypic construct. Viable S. aureus (1×106 CFU) (a–c) or UV-killed S. aureus (1×107 CFU) (d) were applied on the stratum corneum surface and individual constructs fixed at the indicated time after bacterial application. Skin constructs were then sectioned and stained with anti-S. aureus (green) to visualize bacteria. Keratinocyte nuclei were counter stained with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) (blue). Scale bar=20 μm. Arrows indicate immunoreactivity for S. aureus under the epidermal surface when live bacteria were applied to the surface.
