Figure 6. Skin barrier repair decreases S. aureus entry into the dermis and suppresses subsequent immune response in skin with FLG mutation.
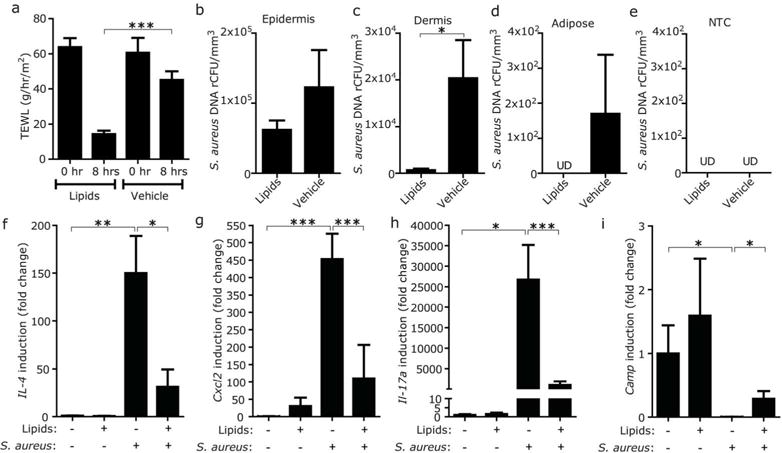
(a) Effect of the application of barrier repair formula of ceramide-triple lipid mixture on TEWL from FLGft/ft Balb/c mice sensitized with OVA. TEWL was measured 4 hrs after application of barrier repair lipids or vehicle. (b–e) Effect of the application of barrier repair lipid mixture on entry of S. aureus into the skin of FLGft/ft Balb/c mice with AD-like inflammation. Entry of S. aureus (ATCC3555) into epidermis (b), dermis (c) and adipose tissue (d) was tracked 4 hrs after application of barrier repair lipids or vehicle. NTC was simultaneously processed as negative control (e). Data represent mean ± SEM of results from 5–6 independent experiments. (f–i) Effect of the application of barrier repair lipid mixture on cytokine and Camp inductions after epicutaneous application of S. aureus on the OVA-sensitized skin of FLGft/ft Balb/c mice. Data represent mean ± SEM of results from 6–7 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **<0.01, ***P<0.001. UD=undetectable
