Figure 8.
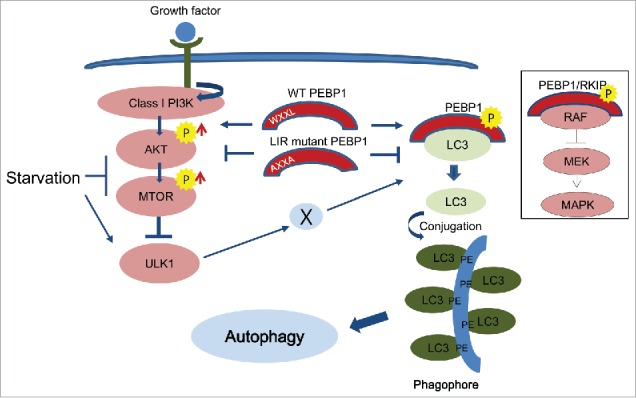
Schematic illustration of PEBP1-mediated autophagy pathways. PEBP1 negatively regulates autophagy during starvation. First, PEBP1 directly interacts with LC3 via its WXXL motif to inhibit LC3 lipidation with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and consequently prohibit autophagy. Second, the PEBP1-LC3 complex stimulates the AKT-MTORC1 pathway, which is a major negative regulator for autophagy. Whereas wild-type (WT) PEBP1 tends to form inactive complexes with cytosolic LC3 via a LIR (WXXL) motif, the LIR mutant PEBP1 (AXXA) protein fails to form the PEBP1-LC3 complex, leading to LC3 lipidation for autophagy. In addition, deactivation of the AKT-MTORC1 pathway by the LIR mutant PEBP1 (AXXA) could involve ULK1 activation and consequently promote autophagy through modulation of the PEBP1-LC3 complex and PEBP1 phosphorylation by an unidentified kinase (X). The general role of PEBP1/RKIP and its phosphorylation at Ser153 (indicated by P) as a MAPK/ERK inhibitor is depicted in the rectangle.
