Figure 2.
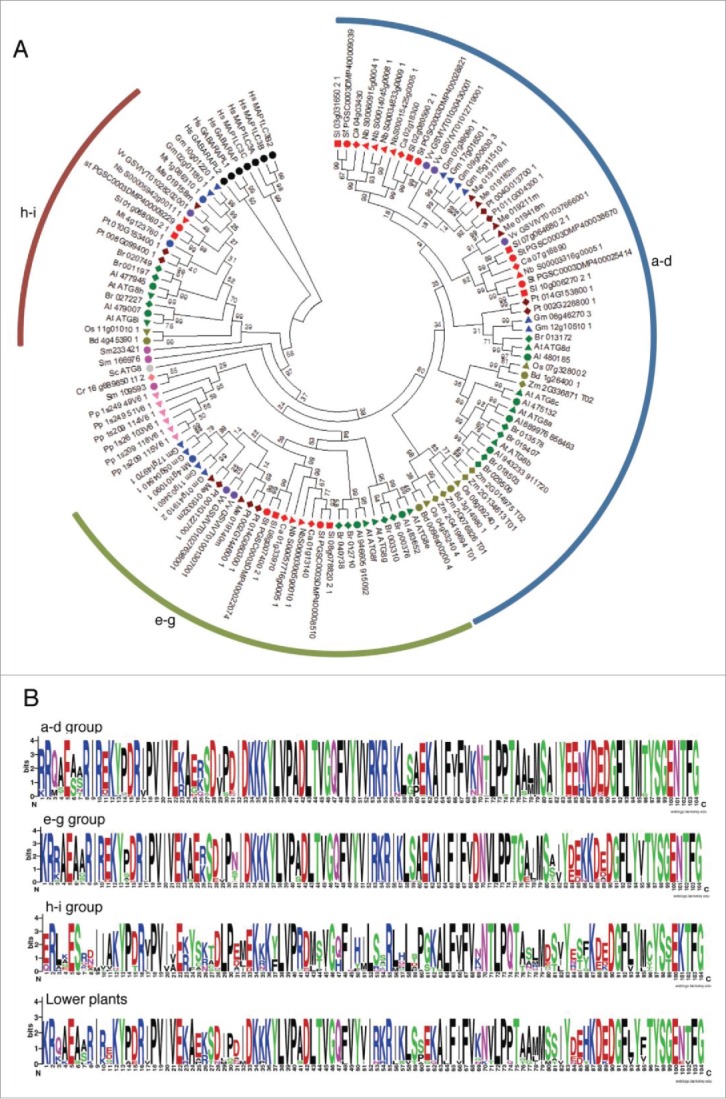
Analysis of ATG8s from different plant species. (A) A phylogenetic tree was constructed using nucleotide sequences and amino acid alignments of ATG8 domains. Maximum likelihood model was used and bootstrap analysis was performed with 1000 replicates to support each branch. Same colors mean related species and the 3 ATG8 subgroups (a to d, e to g, and h and i) were marked as arcs. For different species abbreviations, see Fig. 1A legend. (B) Domain sequences in each subgroup of ATG8. Amino acid sequences of plant ATG8s of each subgroup were aligned and the domain sequences were extracted according to PFAM database (PF02991). Single insertion sequence was removed and the motif logo was created using the alignment. The height of symbols indicates the sequence conservation and residue prevalence of multiple alignment positions.
