Figure 6.
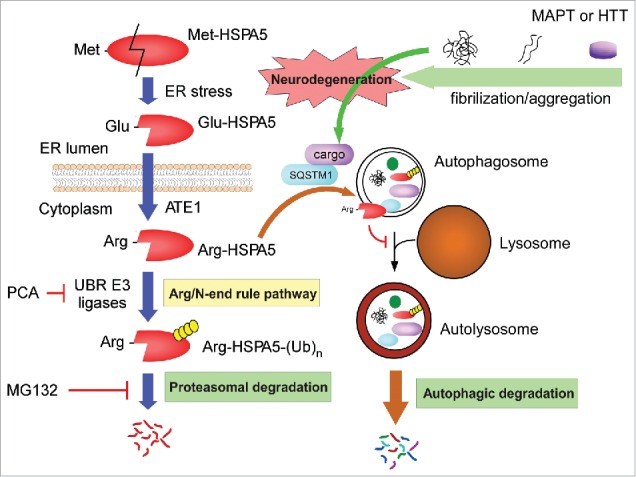
Regulatory roles of the Arg/N-end rule pathway in autophagic flux and protein aggregate clearance. Model illustrating the pro-autophagic and possible neuroprotective roles of the Arg/N-end rule pathway. The ER-residing chaperone protein HSPA5 is cleaved to Glu-HSPA5 under ER stress and translocates to the cytoplasm. ATE1 transfers an Arg residue to the N terminus of Glu-HSPA5, generating Arg-HSPA5. Arg-HSPA5 directly interacts with SQSTM1 and ultimately other cargo proteins, which include various aggregation-prone proteins such as MAPT and HTT, and guides them into the autophagosome for autophagic clearance. At the relatively late stage of autophagy, Arg-HSPA5 is recognized by UBR N-end rule E3 ligases and degraded by the 26S proteasome, which allows autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Therefore, the Arg/N-end rule pathway is a positive regulator of cellular autophagic flux and may have a protective role against proteotoxic protein-mediated neurodegeneration.
