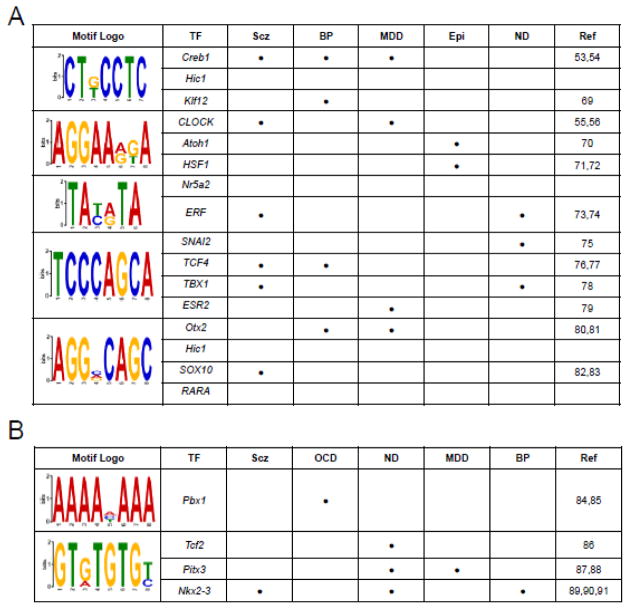
Figure 3.
Identification of DhMR-associated sequence motifs and their putative transcription factors. The DREME suite was used to predict the sequence motifs in hyper-(A) and hypo-(B) DhMRs. Motifs with E-value <10−3 were considered to be significant. Putative binding factors were predicted using SpaMo directly from the DREME suite software package and are listed in the tables shown with their putative transcription factors. The literature (Ref) links of each TF to psychiatric disorders are shown: Scz (schizophrenia); BP (Bipolar Disorder); MDD (Major Depressive Disorder); Epi (Epilepsy); ND (Neuronal Differentiation); OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Disorder) (Aston et al., 2005; Basmanav et al., 2015; Butts et al., 2014; Castilhos et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2014b; Chiang et al., 2015; Forero et al., 2016; Forrest et al., 2013; Goes et al., 2015; Grados et al., 2014; Gurung and Prata, 2015; Hattori et al., 2014; Johansson et al., 2016; Jukic et al., 2015; Keyes et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2014; Le-Niculescu et al., 2009; Lisowski et al., 2013; Mencarelli et al., 2008; Nestadt et al., 2012; Rivolta et al., 2014; Rotheram-Fuller et al., 2010; Schlaudraff et al., 2014; Shi et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2014; Wei et al., 2015; Wockner et al., 2014).