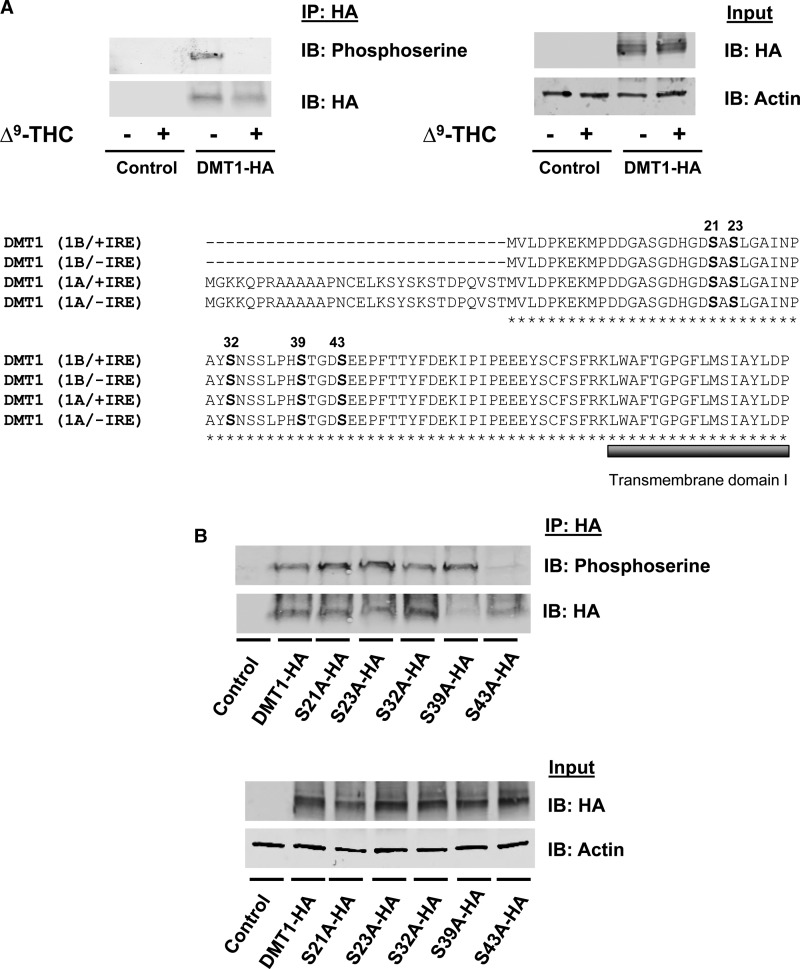
Figure 4. Serine phosphorylation of DMT1 is blocked by Δ9-THC.
(A) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with an empty vector or DMT1-HA. Cells were preincubated with a phosphatase inhibitor in PBS++ at 37°C for 15 min and then spun down, resuspended in uptake buffer containing a phosphatase inhibitor with 50 μM Δ9-THC or control vehicle (0.5% DMSO, v/v) at 37°C for 20 min. After immunoprecipitation with anti-HA, samples were immunoblotted to determine serine phosphorylation (IP: HA and IB: Phosphoserine) compared with immunoprecipitated DMT1-HA protein (IP: HA and IB: HA). Total cell lysates from the same samples (Input) were used to detect DMT1-HA protein (IB: HA) and actin was used as a loading control (IB: Actin). Amino acid alignment between mouse DMT1 isoforms (1B/+IRE, 1B/−IRE, 1A/+IRE and 1A/−IRE) was generated with ClustalW. The predicted phosphorylation sites are located in a conserved region (marked with bold letters) before the first predicted transmembrane domain (marked with a bold, gray line under amino acid sequence). (B) HEK293 cells were transfected to express DMT1-HA and serine mutants (S21A-HA, S23A-HA, S32A-HA, S39A-HA and S43A-HA). DMT1 was immunoprecipitated from the cell lysates with anti-HA antibody (IP: HA) and immunoblotted with antiphosphoserine antibody (IP: HA and IB: Phosphoserine). Blots were then stripped and reprobed with anti-HA (IP: HA and IB: HA) as a loading control. Total cell lysates from the same samples (Input) were used to detect total abundance of DMT1-HA protein and actin.