Figure 1.
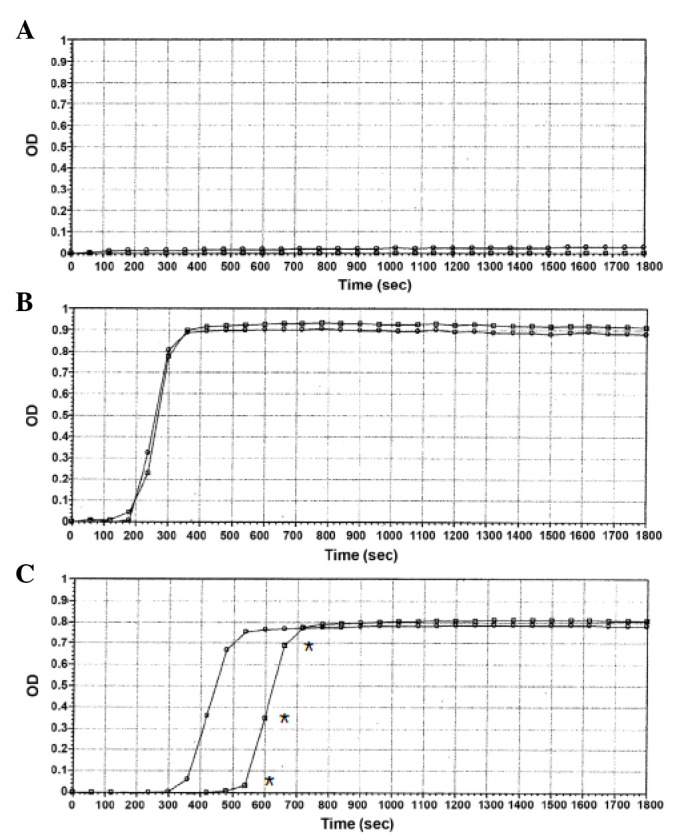
Coagulation rate of human plasma containing MPs from 50 cancer patients or 10 healthy volunteers. Plasma samples were incubated with saline or anti-FVII antibody. Coagulation was initiated by the addition of calcium chloride (t=0) and monitored for 1,800 sec. (A) No clotting was observed when plasma samples from healthy subjects were re-calcified in the presence or absence of anti-FVII antibody. The graph refers to one single experiment and is representative of 10 other consistent independent experiments. (B) For 30 cancer patients, the addition of an anti-FVII antibody to the plasma samples did not significantly affect (P>0.05) the clotting time compared with samples treated with saline alone. The graph displayed refers to a single experiment and is representative of 30 other consistent independent experiments. (C) For 20 cancer patients, the presence of an anti-FVII antibody in plasma samples induced a significant (*P<0.05) lengthening (~43%) of the plasma clotting time compared with the control, which indicated the presence of tissue factor on the surface of MPs. The graph refers to a single experiment and is representative of 20 other consistent independent experiments. OD, optical density; MPs, microparticles; FVII, factor VII.
