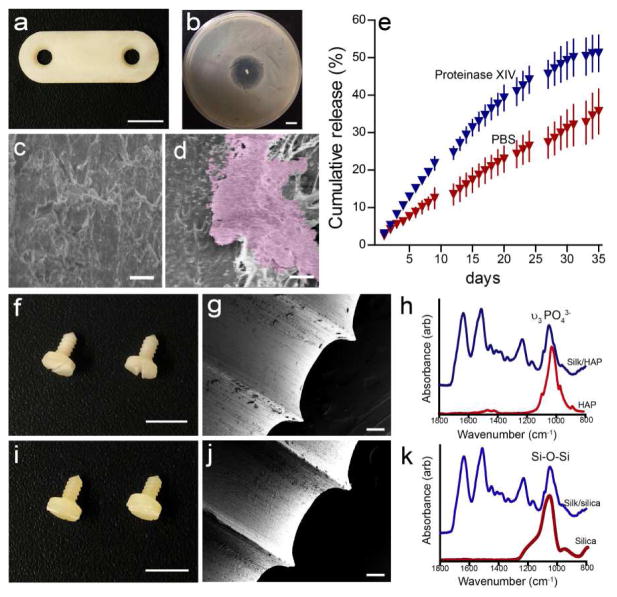
Figure 4.
Silk-based antimicrobial and biocomposite orthopedic devices. (a) Two-hole plate containing 5% (wt/wt) ciprofloxacin (scale = 5 mm). (b) A clear zone of inhibition formed around ciprofloxacin releasing silk rods against S. aureus cultures (scale = 1mm). SEM of biofilm on (c) ciprofloxacin-loaded and (d) pure silk pins, scale = 10 μm. (e) The cumulative release of ciprofloxacin from ciprofloxacin-loaded silk rod over 36 days. (f and i) Optical images, (g and j) SEM images and (h and k) FTIR spectra of the (f–h) silk/HAP (90/10 wt/wt) and (i–k) silk/SiO2 (90/10 wt/wt) biocomposite screw with bone screw thread. Scale = 5 mm in d and g and 100 μm in e and h, respectively.