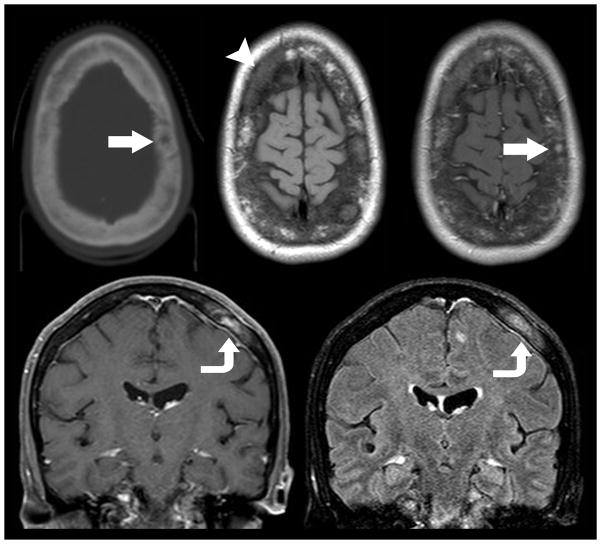
Figure 10.
Mixed lytic and sclerotic metastatic disease of the calvarium. Non-contrast axial CT (top left) in a 49 year old woman with metastatic breast cancer demonstrates a mixed lytic sclerotic diploic space mass (arrow). Subsequent pre (top middle) and post-contrast enhanced (top right) MR imaging demonstrates extensive loss of fatty diploic space marrow (arrow head) with evidence of focal contrast enhancing mass (arrow). Coronal T1 weighted post contrast (bottom left) and FLAIR (bottom right) MR imaging demonstrates the enhancing diploic space mass with direct extension to the subjacent dura (curved arrow) suggesting parchymeningeal involvement. Contrast enhanced MR imaging is superior to CT in the detection of metastatic disease within the diploic space, dura, and brain.