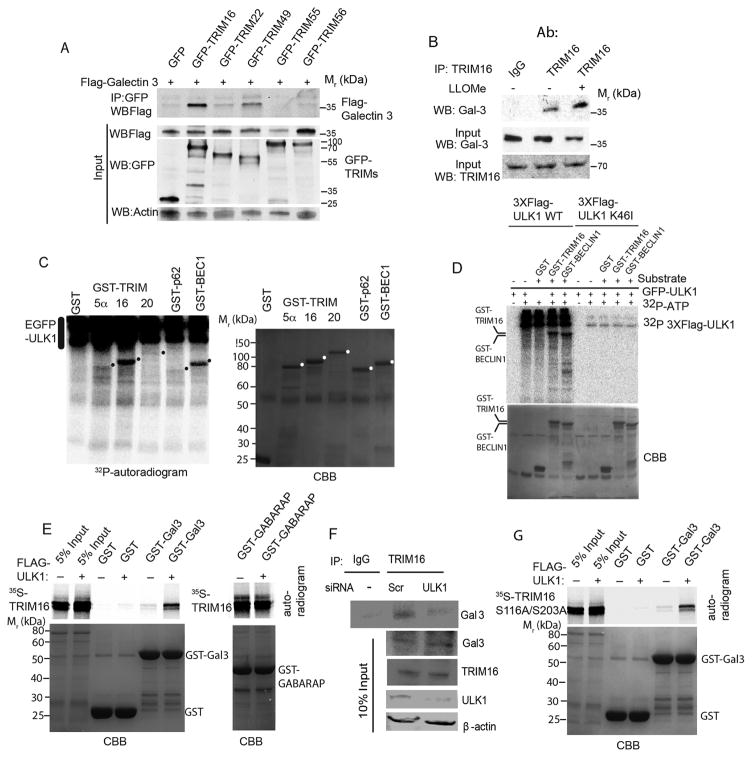
Figure 3. TRIM16 is phosphorylated by ULK1 and interacts with Galectin-3 in the presence of ULK1 as a platform.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) analysis of interaction between Galectin-3 and a panel of TRIMs in HEK293T cell lysates expressing GFP or GFP-TRIM fusions and Flag-Galectin-3. (B) Co-IP analysis of endogenous TRIM16 and endogenous Galectin-3 in the absence and presence of LLOMe. (C) Indicated GST-fusion proteins were incubated in a phosphorylation reaction (with γ32P ATP) with EGFP-ULK1 enriched from HEK293T cells and products separated by PAGE. Left, autoradiogram; right, coommassie brilliant blue (CBB). Dots, position of GST-fusion protein bands on the CBB gel. (D) Flag-ULK1 wt or K46I catalytic ULK1 mutant were incubated with GST fusion protein substrates and processed as in C. (E) In vitro translated and radiolabeled [35S] myc-HA-TRIM16 wild type incubated with potential interactors in the presence (+) or absence (−) of Flag-ULK1 and cold ATP, GST pulldowns performed and amount of [35S] radiolabeled Myc-HA-TRIM16 determined by PAGE and autoradiography. Amounts of GST fusion proteins are shown in coommassie brilliant blue (CBB)-stained gels (F) Co-IP analysis of interactions between endogenous TRIM16 and Gal3 proteins in HeLa cells knocked down for ULK1 by siRNA. (G) GST pulldown analysis as in E, using [35S] myc-HA-TRIM16-S116A/S203A mutant instead of wild type TRIM16. Note that both wt (in E) and the ULK1-non-phosphorylatable TRIM16-S116A/S203A (in G) mutant promote association between TRIM16 and Galectin-3.