Figure 4.
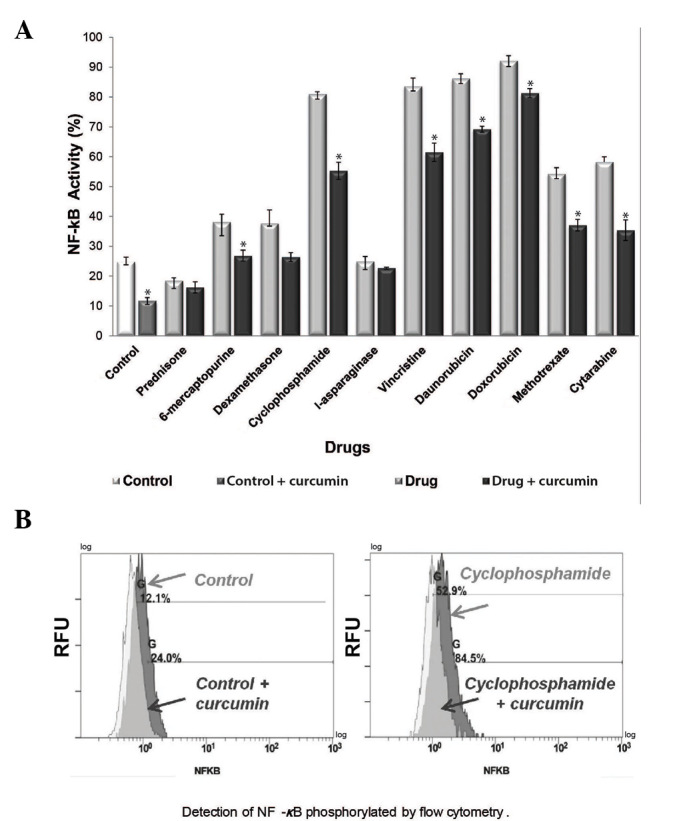
Effect of curcumin and chemotherapy on NF-κB activity. (A) Comparison of NF-κB activity in the groups treated with chemotherapeutic agents alone and in those co-treated with 20 µM curcumin. *P<0.05 vs. control. (B) Treatment with 20 µM curcumin increased NF-κB activity in REH cells, and this increase was most evident in the cyclophosphamide-treated group compared with the cyclophosphamide + curcumin-treated group. NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B.
