Figure 5.
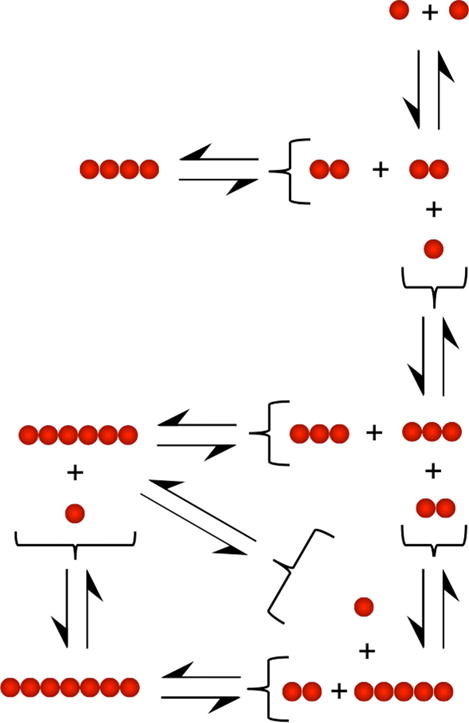
Model of Aβ42 oligomerization. The association and dissociation patterns observed for oligomer orders 2–7 (Figures 2–4 and Figures S1–S3), along with the occurrence frequencies for each oligomer (Tables S1–S5), were used to produce a model of oligomer formation. Simple monomer addition models, akin to actin polymerization,30 do not appear to explain these data. Instead, key roles are played by monomers, dimers, and trimers, which appear to act as building blocks for higher-order oligomers.
