Table 2.
Sample characteristics for participants in each cohort.
| Variable | Language for Learning (n = 201) | Early Home Learning Study (n = 218) |
|---|---|---|
| Parent age, years, mean (SD) | 35.3 (4.4) | 32.6 (5.1) |
| Child age, months, mean (SD) | 24.4 (1.1) | 16.2 (9.3) |
| Child female, n (%) | 95 (47.0) | 113 (51.8) |
| Parent marital status n, (%) | ||
| Single/separated/divorced | 11 (5.5) | 17 (7.8) |
| Married/de facto | 190 (94.5) | 201 (92.2) |
| Household unemployment n (%)‘ | 10 (5.0) | 18 (8.3) |
| Parent education, n (%) | ||
| Higher education | 93 (46.7) | 112 (51.4) |
| No higher education | 106 (53.3) | 106 (48.6) |
LOTE, 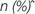
|
19 (9.5) | 46 (21.1) |
| Household income p/a, n (%)∗ | ||
| <$46,800 | 38 (19.3) | – |
| $46,800–$70,200 | 69 (35.0) | – |
| >$70,200 | 90 (45.7) | – |
| <$36,400 | – | 26 (12.0) |
| $36,400–51,999 | – | 36 (16.6) |
| ≥ $52,000 | – | 147 (67.7) |
| SEIFA#, mean (SD) | 1026.6 (54.1) | 984.2 (57.9) |
‘Single parent unemployed or both parents unemployed; ˆLanguage other than English; ∗Different categories of income were administered for each sample; #Socio-Economic Index for Areas (SEIFA) Disadvantage score is an indicator of relative disadvantage, based on postcode of residence, accounting for low income, low educational attainment and high unemployment. Lower index scores indicate greater disadvantage.
