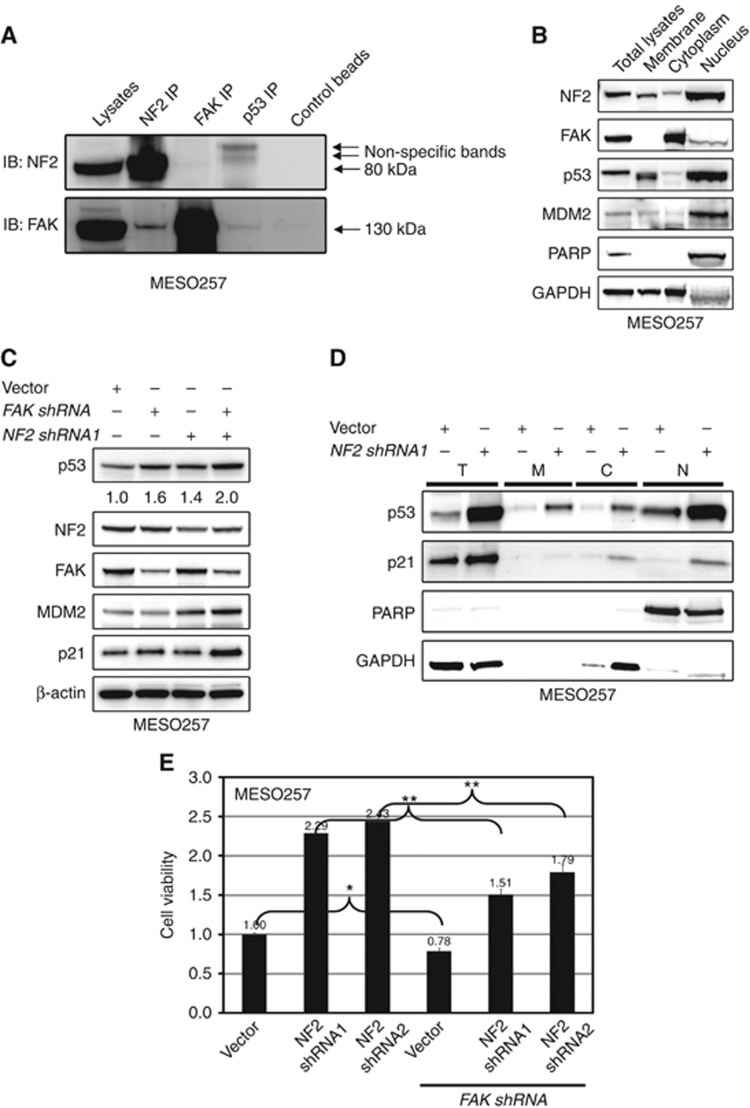
Figure 6.
NF2 regulates the interaction of FAK–p53 and MDM2–p53. (A) The NF2–FAK complex was evaluated in MESO257 by NF2 and FAK immunoprecipitation followed by FAK and NF2 immunoblotting. (B) Nuclear localisation of NF2, FAK, p53, and MDM2 was evaluated in MESO257 by immunoblotting. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) is a nuclear localisation control, and GAPDH is a cytoplasmic control. (C) In MESO257 with stable NF2 shNRA expression, p53, NF2, FAK, MDM2, and p21 expression were evaluated by immunoblotting after FAK shRNA knockdown for 72 h. β-Actin staining is a loading control. p53 expression quantifications are standardised to the empty vector control. (D) Expression of p53 and p21 was evaluated in MESO257 cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus with stable NF2 shNRA expression by immunoblotting. (E) Cell viability was evaluated by a cell titre Glo ATP-based luminescence assay in MESO257 with stable expressed NF2 shRNA, at 72 h post-infection with FAK shRNA. Data were normalised to empty lentivirus infections, and represent the mean values (±s.d.) from quadruplicate cultures. Statistically significant differences between untreated control and treatments or between vector control and FAK shRNA or NF2 shRNA and NF2+FAK shRNA are presented as *P<0.05, **P<0.01.