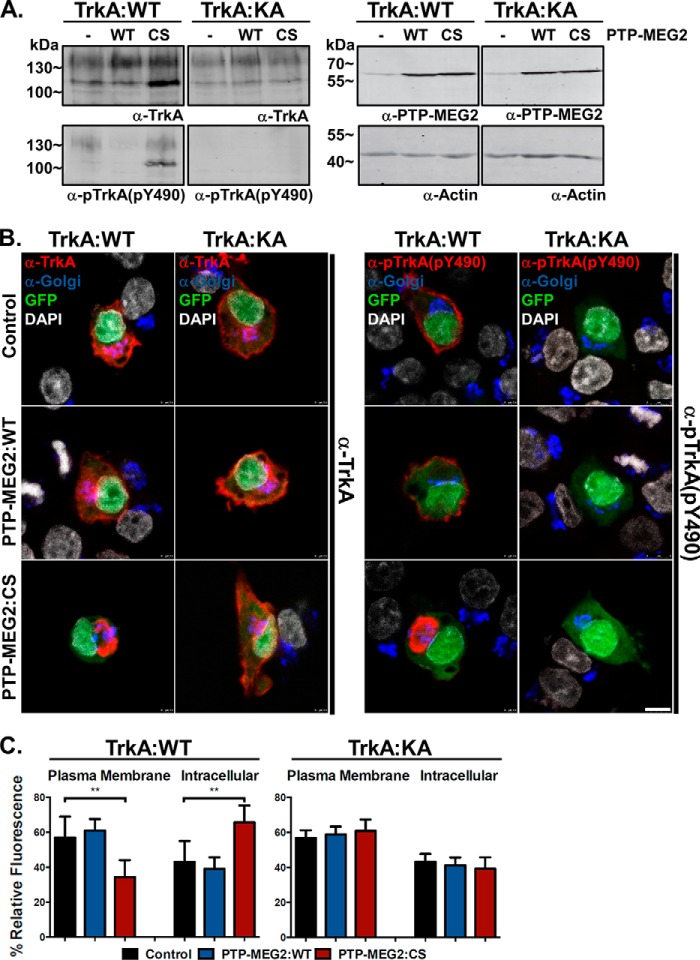
FIGURE 5.
The kinase-dead TrkA mutant can bypass the transport block and relieve the perinuclear accumulation caused by the PTP-MEG2:C515S mutant. A, immunoblot showing similar expression levels but contrasting phosphorylation status of TrkA:WT and TrkA:K547A with anti-TrkA and anti-pTrkA antibodies as indicated. TrkA:K547A shows no detectable autophosphorylation. The two TrkA proteins were either expressed alone or co-expressed with PTP-MEG2:WT or PTP-MEG2:C515S as indicated. The actin level in each sample served as a loading control and molecular mass standards (in kilodaltons) are indicated on the left. B, representative confocal microscopy images of PC12 cells overexpressing TrkA:WT or the kinase-dead TrkA:K547A mutant, which was co-expressed with GFP alone or with PTP-MEG2:WT or the PTP-MEG2:C515S mutant as indicated. The cells were stained with antibodies for TrkA, pTrkA, and the Golgi markers GM130 and TGN38 as well as with DAPI for the nucleus. Scale bar = 2.5 μm. C, quantification of the percentage of total TrkA and TrkA:K547A at the plasma membrane versus the intracellular compartments in control cells, PTP-MEG2:WT-expressing cells, and PTP-MEG2:CS-expressing cells. In each case, the relative fluorescence intensity from multiple confocal images (n = 5) like those in B was quantified (**, p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons). Error bars indicate standard deviation.