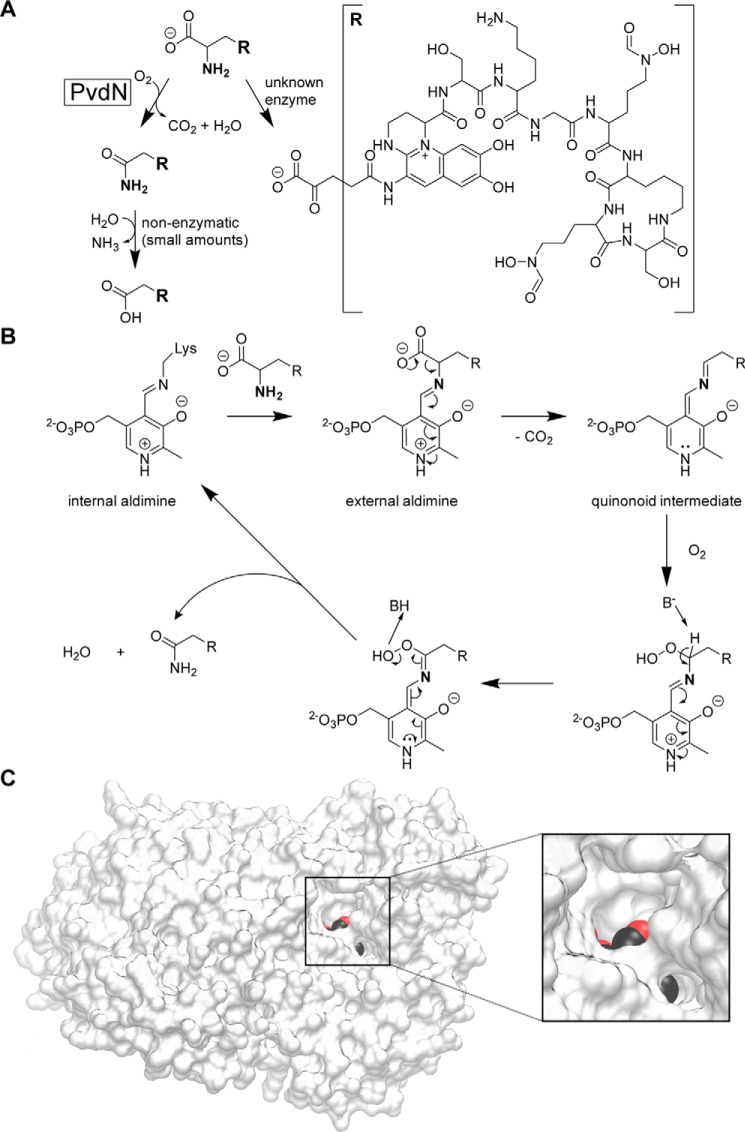
FIGURE 7.
Role and putative mechanism of PvdN catalysis in the biosynthesis of pyoverdines. A, branched modification pathway of the side chains at the N3-position of the pyoverdine fluorophore. B, likely mechanism of PvdN-catalyzed PLP-dependent oxidative decarboxylation under retention of the amine nitrogen. See “Results” for details. C, as expected for the proposed model, two channels connect the PLP-containing active site cavity with the surface. PLP atoms are colored to visualize the channels, which both lead to the reactive side of the cofactor. For this figure, PvdN of P. fluorescens A506 was homology-modeled using the available PvdN structure (PDB5i90; ∼62% sequence identity; global model quality estimation (GMQE) 0.79 (44–46)) as template. The image was generated using the VMD software (47).