FIGURE 9.
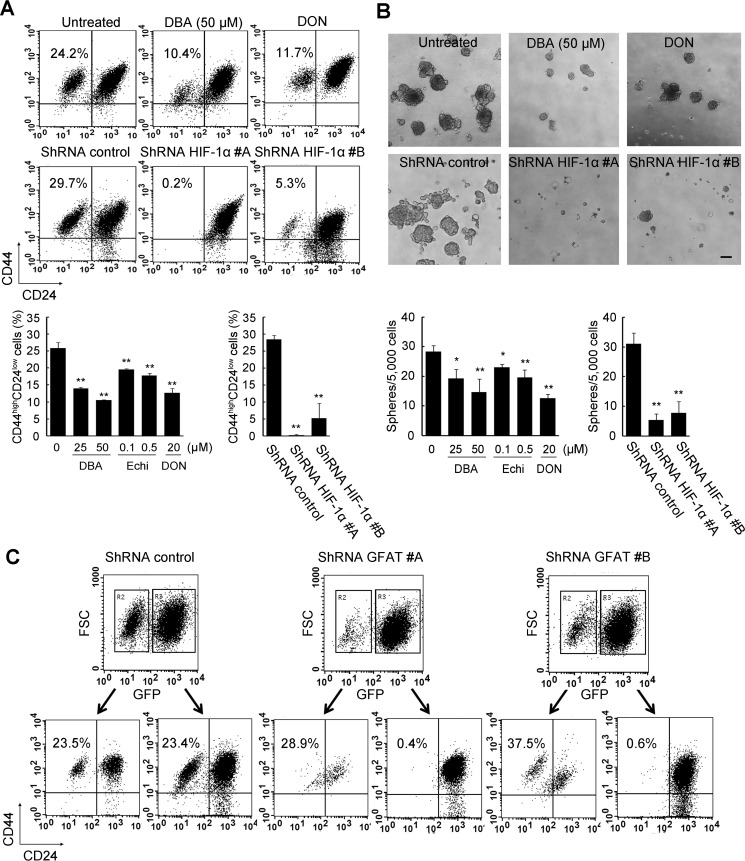
Significance of HBP and HIF-1 signaling in CSC-like properties. A, flow cytometric analysis of the CD44high/CD24low subpopulation after pharmacological inhibition or gene silencing of HIF-1α. Has2ΔNeo cells were treated with HIF-1α inhibitors (25 or 50 μm DBA and 0.1 or 0.5 μm echinomycin (Echi)) for 7 days. Has2ΔNeo cells were also treated with a GFAT inhibitor (20 μm DON) for 7 days. Treated cells were analyzed for CD24 and CD44 expression by flow cytometry. HIF-1α knockdown cells were also subjected to flow cytometric analysis. Data represent the mean ± S.D. (error bars) of three independent experiments. **, p < 0.01 as compared with untreated or control cells. B, mammosphere formation after pharmacological inhibition or gene silencing. Has2ΔNeo cells treated with an HIF-1α or GFAT inhibitor were examined for mammosphere formation. HIF-1α knockdown cells were also examined for mammosphere formation. Representative images of mammospheres were taken, and mammosphere number was counted under a phase-contrast microscope. Scale bar, 100 μm. Data represent the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. C, flow cytometric analysis of the CD44high/CD24low subpopulation after gene silencing of GFAT1. Two different shRNAs (#A and #B) against murine GFAT1 mRNA were introduced into Has2ΔNeo cells using a lentiviral vector. The introduced cells were analyzed for GFP expression. Both GFP-positive and -negative cells were further analyzed for CD24 and CD44 expression by flow cytometry.