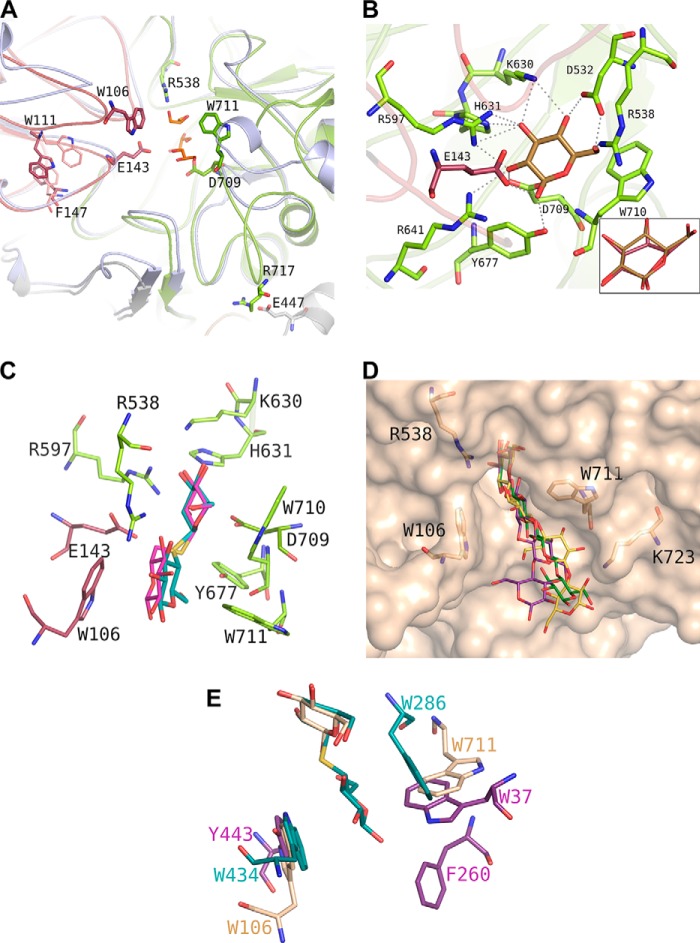
FIGURE 3.
GlyA1 active site architecture. A, detail of the loops surrounding its active site from the (α/β)8 barrel (green) and the (α/β)6-sandwich (raspberry) domains, superimposed onto the T. neapolitana β-glucosidase (8) (pale blue). Three glycerol molecules from the cryobuffer found in the GlyA1 crystals are shown in orange. Asp-709 and Glu-143 are the nucleophile and the acid/base catalyst, respectively. Main features of GlyA1 are the extended loop containing Asp-709, which includes Trp-711 and the ion pair Arg-717–Glu-447 fixing it to the unique long arm and a highly flexible loop containing Trp-106. Two different conformations found among the crystals at Trp-111 and Phe-147 are highlighted. B, detail of the atomic interactions defining subsite −1. A glucose molecule is shown in gold. Xylose binds in the same relaxed chair conformation, and only interaction of the glucose O6 hydroxyl is missing. Inset, binding mode of galactose in a semi-chair conformation by flattening of the C4 atom that has the axial hydroxyl substituent and keeping the same interaction pattern. C, thiocellobiose (cyan) and thiogentibiose (pink) modeled at the active site by structural superimposition to the previously determined β-d-glucan glucohydrolase barley complexes (PDB entries 1IEX and 3WLP (34)), delineating putative subsite +1. D, molecular surface of the GlyA1 active site, with relevant residues as sticks. Three different β-1,4/β-1,3-linked tetraglucosides have been manually docked by superposition of their non-reduced end to the experimental glucose: a cellotetraose, as found in PDB entry 2Z1S (green); a Glc-4Glc-3Glc-4Glc (purple), and a Glc-4Glc-4Glc-3Glc (yellow), as built by the on-line carbohydrate-building program GLYCAM (45) and exported in its minimum energy state. E, superposition of GlyA1-Glc structure (beige) with those reported for T. reesei β-glucosidase (purple) (12) and barley β-d-glucan glucohydrolase complexed with thiocellobiose (cyan) (34).