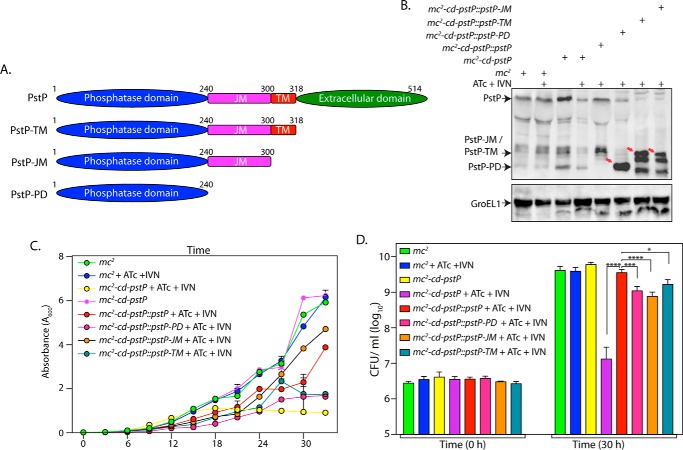
FIGURE 5.
Deletion of different PstP domains leads to mildly compromised rescue. A, schematic depiction of domain structure of PstP. PD, phosphatase domain; JM, juxtamembrane; TM, transmembrane. B, M. smegmatis mc2, mc2-cd-pstP, mc2-cd-pstP::pstP-TM, mc2-cd-pstP::pstP-JM, and mc2-cd-pstP::pstP-PD cultures were initiated at an A600 of 0.1 in the absence or presence of ATc + IVN (50 ng/ml ATc + 5 μm IVN) for 12 h. WCLs were prepared, and 40 μg (for PstP) and 20 μg (for GroEL1) of lysates were resolved on SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membrane, and probed with α-PstP and α-GroEL1 antibodies. C, mc2, mc2-cd-pstP, mc2-cd-pstP::pstP-TM, mc2-cd-pstP::pstP-JM, and mc2-cd-pstP::pstP-PD cultures were initiated at an A600 of 0.02, and growth was monitored in the absence or presence of ATc + IVN every 3 h for 30 h. Growth analysis is plotted as the mean with error bars representing S.D. D, cfu enumeration was performed for mc2, mc2-cd-pstP, mc2-cd-pstP::pstP-TM, mc2-cd-pstP::pstP-JM, and mc2-cd-pstP::pstP-PD from the cultures in C at 0 and 30 h. Data were plotted as the mean with S.D., and significance was calculated using two-way ANOVA with p < 0.0001 (****), p < 0.001 (***), and p < 0.05 (*).