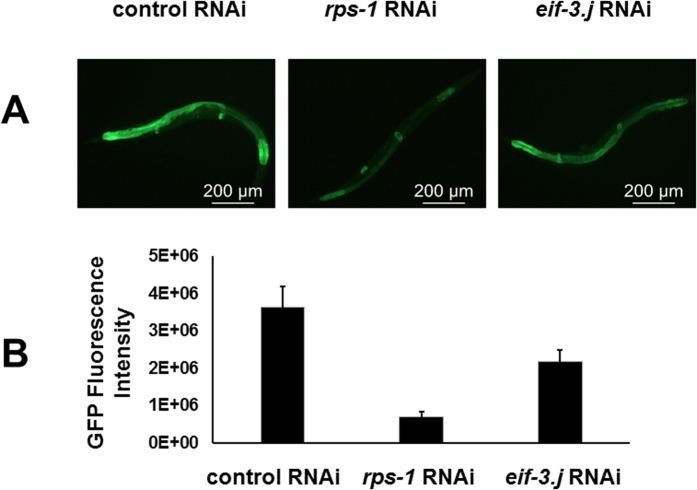
Figure 4. Knockdown of rps-1 or eif-3.j by RNAi reduces the XBP-1-dependent UPR in octr-1 mutant animals.
(A) Images of octr-1(ok371);Phsp-4::GFP(zcls4) animals. Animals were grown on double-stranded RNA for vector control or dsRNA for rps-1 or eif-3.j, and young adult animals were exposed to P. aeruginosa PA14. Animals that best represent the fluorescence level of the population were shown. (B) GFP quantification of octr-1(ok371);Phsp-4::GFP(zcls4) animals exposed to P. aeruginosa PA14. Binary mean intensity of the region of interest (ROI) that corresponds to an entire animal was measured by Image J software. n = 10–20 animals, error bars represent SEM. A two-sample t test was performed to compare the fluorescence intensity between populations. rps-1 RNAi versus control RNAi: p = 6.1 × 10−10; eif-3.j RNAi versus control RNAi: p = 4.8 × 10−7. p values < 0.05 are considered significant. Significant knockdown of rps-1 or eif-3.j expression by RNAi was confirmed by qRT-PCR (p < 0.001, Figure S3).