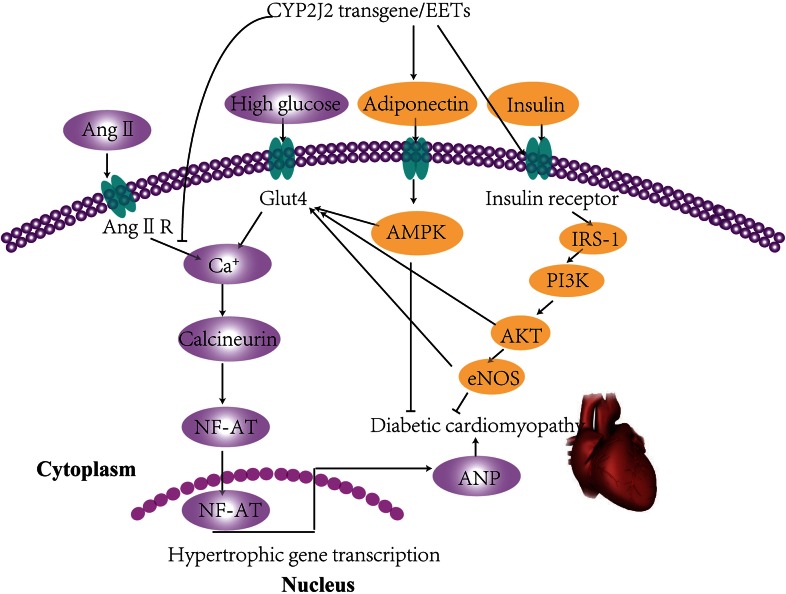
FIGURE 2.
Signaling mechanisms involved in cardiovascular complications of insulin resistance. High glucose and Ang II increase intracellular calcium, promote NF-AT into the nucleus, and enhance transcription leading to cardiac hypertrophy. CYP2J2 overexpression increases the transfer of Glut4 to the cell membrane and also activates IRS-1/PI3K/AKT eNOS and upregulates adiponectin/AMPK signaling pathways, thus reversing the process of cardiac hypertrophy. AKT, protein kinase B; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; Ang II, angiotensin II; Ang II R, angiotensin II receptor; ANP, atrial natriumtic peptide; CYP2J2, cytochrome P450 2J2; EET, epoxyeicosatrienoic acid; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; Glut4, glucose transporter type 4; IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate-1; NF-AT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Adapted from reference 24 with permission.