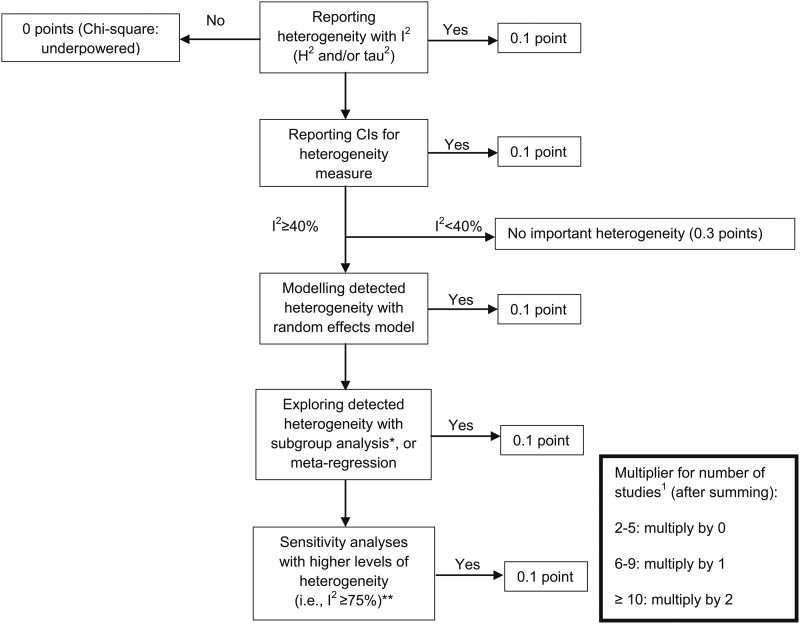
FIGURE 3.
Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analyses. *Subgroup analyses: assessing whether effect is similar across specific groups of patients or is modified by study and patient characteristics (i.e., checking for consistency across subgroups, checking whether primary results are statistically significant). **Sensitivity analysis: repetition of the primary analysis (i.e., inclusion of some studies is unclear, because full details are not available; or exclusion of the largest study). For multiplier for number of studies, when authors treated men and women as separate studies, these should be treated as one study.