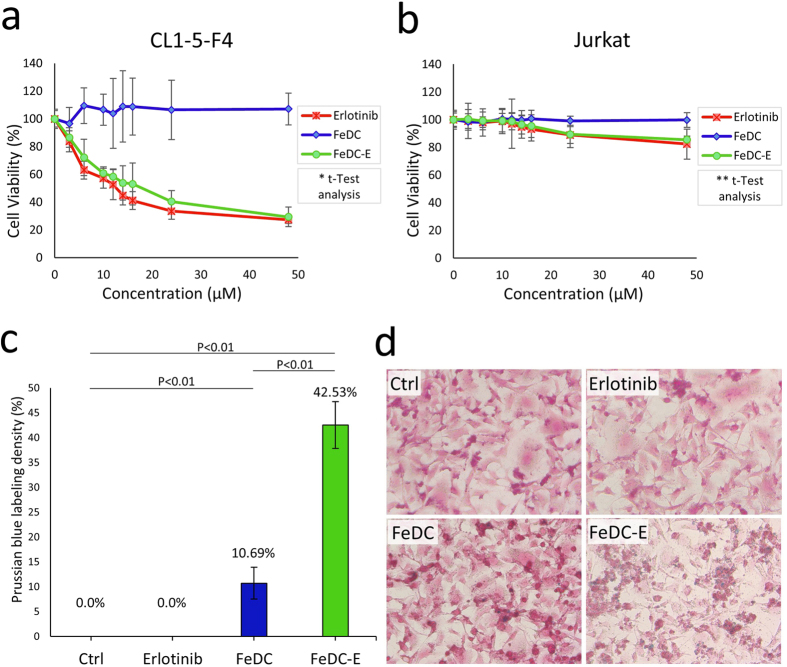
Figure 3. Therapeutic and targeting capabilities of the nanoparticles.
Dose response curves of the cytotoxic activities of Erlotinib, carboxyl group-functionalized dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles (FeDC NPs) and erlotinib-loaded dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles (FeDC-E NPs) against the EGFR overexpressing CL1-5-F4 cells (a) and the EGFR negative Jurkat cells (b). FeDC-E NPs retained the activity of erlotinib and exhibited selective cytotoxic effects against the EGFR overexpressing cancer cells, but not against the other cells. N.B. FeDC NPs formulation was tested using the same volume and iron concentration as the FeDC-E NPs used in the test (because FeDC NPs does not contain erlotinib); however, the scale and label of the X-axis of the FeDC NPs-treated cells were retained for the sake of comparison among tested groups. (c,d) Targeting capability of the nanoparticles detected using the Prussian blue experiments. (c) Percentages of the iron-labeled CL1-5-F4 cells quantified using the ImageJ software. Results showed a 4-fold increase in the cellular uptake of the targeted FeDC-E NPs compared to the non-targeted FeDC NPs due to the targeting capability of erlotinib to EGFR imparted to the FeDC-E nanoparticles. The P-values were calculated using the t-Test method assuming unequal variances. (d) Micrographs of CL1-5-F4 cells processed with the Prussian blue staining procedures. Uptaken nanoparticles are observed as blue spots. *, **Statistical t-test analysis showed non-significant difference among the cytotoxic activities of erlotinib and FeDC-E NPs for any of the tested concentrations for either of the tested cell lines (similar cytotoxic profiles for both treatments), whereas the cytotoxic activities of erlotinib and FeDC-E NPs against CL1-5-F4 cells showed statistical significant difference from their activities against Jurkat cells, and the cytotoxic activities of FeDC NPs did not show statistical significant difference among CL1-5-F4 and Jurkat cells.