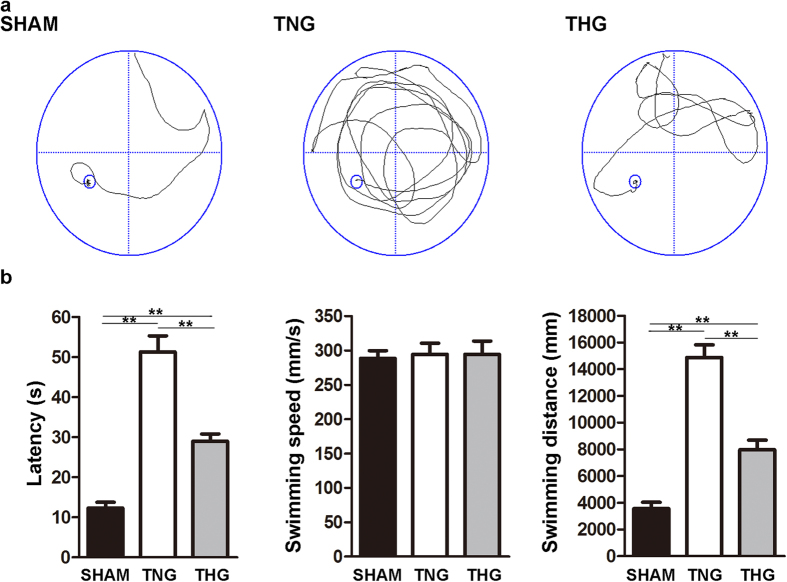
Figure 5. Posttraumatic hypothermia improved learning and memory function recovery after severe TBI.
(a) Typical swimming patterns of the mice in all three groups on the sixth day of the Morris water maze test. (b) The Morris water maze test showed that the latency and the swimming distance of the mice in the THG had significantly decreased compared with those in the TNG 2 weeks after severe TBI. However, swimming speed did not significantly differ among the three groups. The data are represented as the means ± SEM and were analysed using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post hoc test, n = 10, **p < 0.01, THG or sham vs. TNG. TNG, the traumatic brain injury with normothermia group; THG, the traumatic brain injury with hypothermia group.