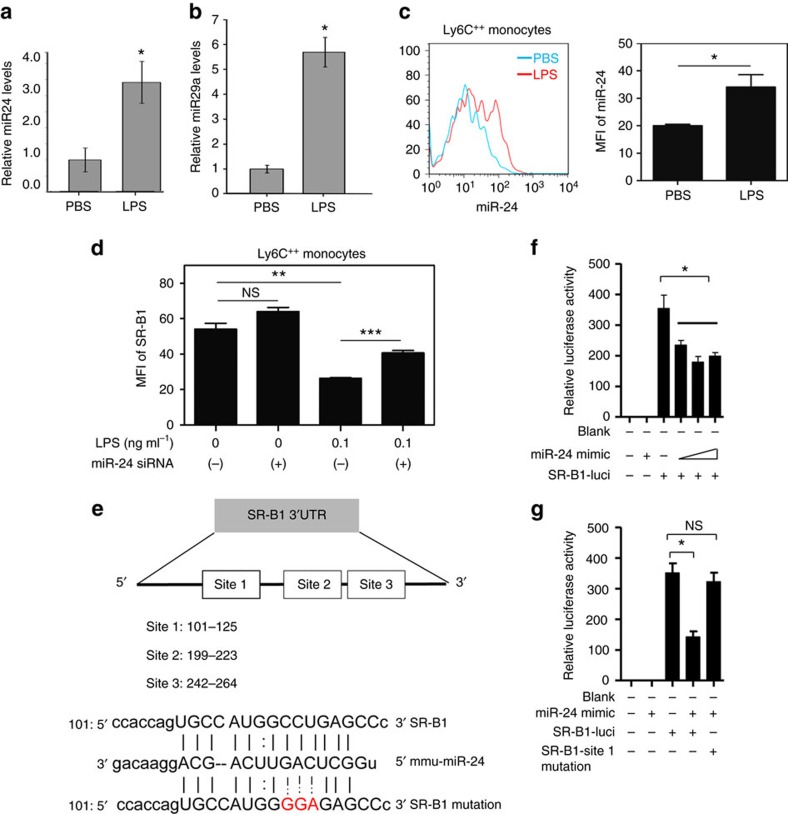
Figure 4. Suppression of SR-B1 in inflammatory monocytes by super-low-dose LPS is dependent on miR-24 induction.
(a,b) ApoE−/− mice were pre-conditioned with PBS or super-low-dose LPS for 4 weeks together with HFD, followed by HFD feeding only for an additional 4 weeks. Total miRs isolated from splenocytes were used for real-time reversre transcriptase–PCR analyses for the relative levels of miR-24 (a) and miR-29 (b). (c) BMMs from C57 BL/6 mice were cultured with M-CSF (10 ng ml−1) in the presence super-low-dose LPS (0.1 ng ml−1) for 3 days and fresh LPS was added to the cell cultures every 2 days. Fluorescent RNA probe for miR-24-3p was added to the cell cultures 16 h before harvesting. The expression levels of miR-24-3p within CD11b+Ly6C++ monocytes were examined by flow cytometry. (d) BMMs from C57 BL/6 mice were cultured with M-CSF (10 ng ml−1) in the presence super-low-dose LPS (0.1 ng ml−1) and miR-24 antagomir was added to indicated cultures. Fresh LPS and antagomir was added to the cell cultures every 2 days. On day 5, cells were harvested and expression levels of SR-B1 within CD11b+Ly6C++ monocytes were analysed by flow cytometry. (e) A schematic illustration of the SR-B1 3′-UTR and potential miR-24-binding sites. (f,g) Luciferase activity assays in 293T cells transfected with either WT or mutant SR-B1 3′-UTR luciferase reporter plasmids in the presence of miR-24 mimic or scrambles. Quantified data are shown from cells with indicated treatment (n=3) and results are representative of three experiments. Error bars show means±s.e.m.; NS, not significant; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001; (a,b,c) Student's t-test; (d,f,g) one-way analysis of variance.