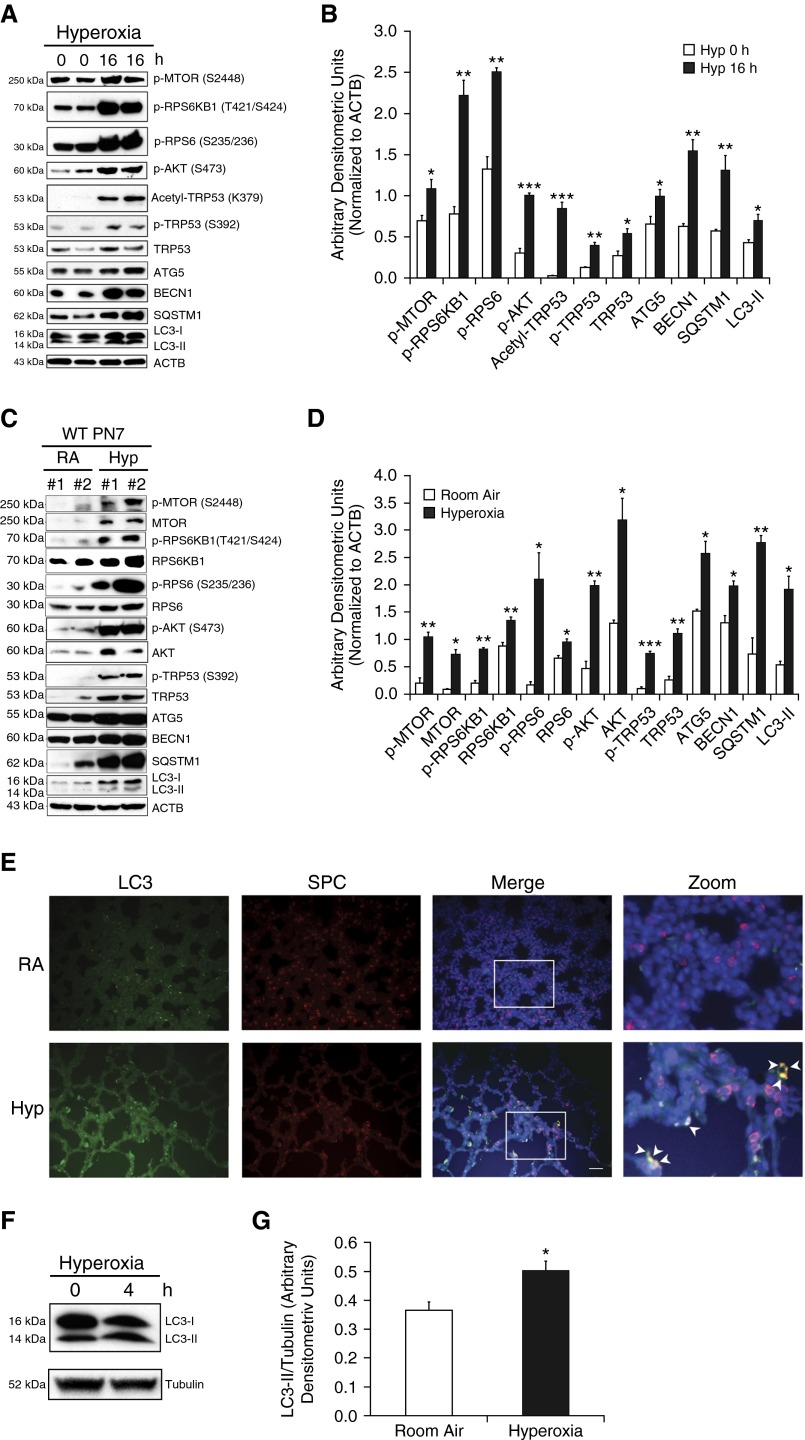
Figure 1.
Hyperoxia induces autophagy in lung epithelial cells and neonatal mouse lungs. (A) Mouse lung epithelial (MLE)-12 cells were incubated with or without the presence of hyperoxia (95% O2 + 5% CO2) for 16 hours. Western blot analysis showed up-regulation of phospho-MTOR (p-MTOR), phospho-ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1 (p-RPS6KB1), phospho-RPS6 (p-RPS6), phospho-Akt (p-Akt), acetyl-transformation–related protein (TRP) 53, phospho-TRP53 (p-TRP53), and TRP53 with concomitant increased expression of autophagy-related (ATG) 5, beclin (BECN) 1, sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1), and light chain-3 (LC3)-II proteins. (B) Densitometric analysis was performed and the expression of observed proteins was normalized to β-actin. (C) Newborn (NB) wild-type (WT) mice were exposed to hyperoxia from Postnatal Days (PNs) 1–7. Western blots showing increased expression of phospho-MTOR, MTOR, phospho-RPS6KB1, RPS6KB1, phospho-RPS6, RPS6, phospho-AKT, AKT, phopsho-TRP53, TRP53, and also increased expression of ATG5, ATG7, SQSTM1, and LC3-I/-II proteins in lung tissues. (D) Densitometric analysis was performed, and the expression of observed proteins was normalized to β-actin. (E) Representative immunofluorescent images depicting colocalization of pro–surfactant protein-C (red) and LC3 proteins (green) in serial sections of hyperoxia-exposed lungs obtained from NB WT mice. Inset images were enlarged, indicating co-localization (yellow) of LC3 in type II alveolar epithelial cells (AECs), as denoted by the arrowheads. (F and G) Western blot analysis demonstrating increased expression of LC3-II (normalized to α-tubulin) in hyperoxia-exposed Embryonic Day (E) 19–20 freshly isolated type II AECs for 4 hours. Values are means ± SEM of a minimum of three independent experiments (in vitro) or four animals in each group (in vivo). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared with respective controls. ACTB, β-actin; Hyp, hyperoxia; MTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; RA, room air; SPC, surfactant protein C.