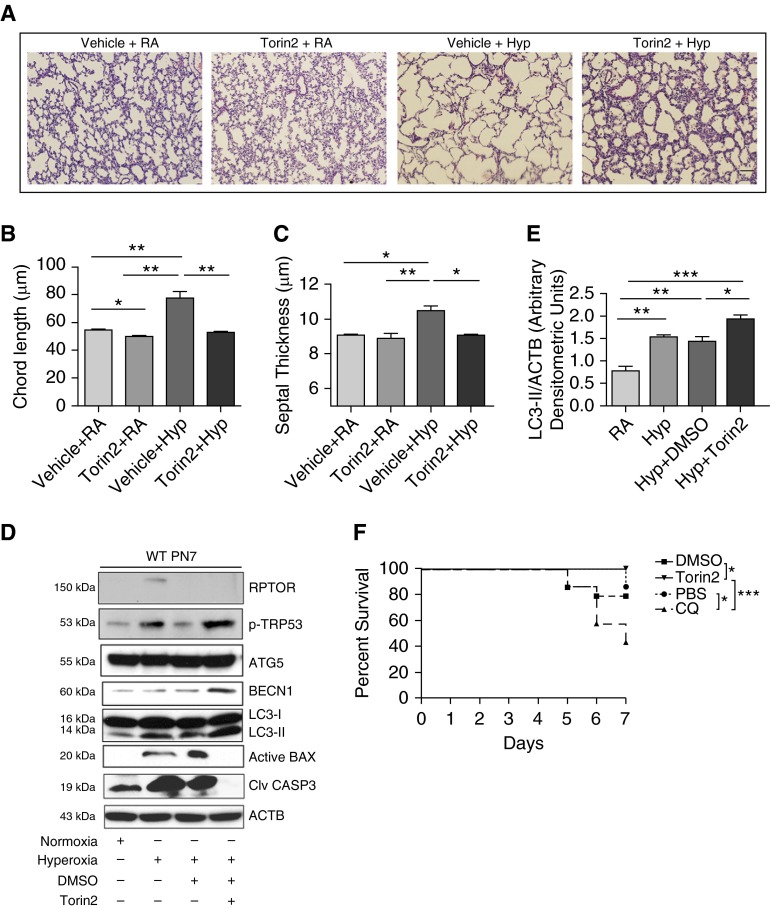
Figure 4.
Torin2 treatment decreased apoptosis and improved lung morphometry and overall survival. (A) Representative images of lung histology (hematoxylin and eosin [H&E] stain) of NB WT mice treated with Torin2 (20 mg/kg; twice daily) and exposed to RA or 100% O2 and survived till PN7. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B and C) Morphometric analyses of lung histology sections of NB WT mice exposed to RA or survived 100% O2 at PN7. Alveolar size expressed as chord length, and septal thickness were analyzed using Image J software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD). (D) Western blot analysis of regulatory-associated protein of mechanistic target of rapamycin (RPTOR), TRP53, ATG5, BECN1, LC3-II, proapoptotic active Bax, and cleaved caspase (CASP) 3 was performed on total lungs obtained from NB WT mice treated with Torin2 and exposed to RA or hyperoxia until PN7. (E) Densitometric analysis was performed and the expression of LC3-II was normalized to ACTB. (F) Effect of Torin2 and CQ on survival of NB WT mice in hyperoxia at PN7. Survival data showing 100% survival of Torin2-treated NB WT mice exposed to hyperoxia, at PN7. NB WT and CQ-treated mice had 85 and 42.8% survival rates, respectively, at PN7. A minimum of 10 animals was used in each group. Values are means ± SEM of a minimum of three observations (in vitro experiments) or four animals (in vivo experiments). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ANOVA. DMSO, vehicle for Torin2; PBS, vehicle for CQ.