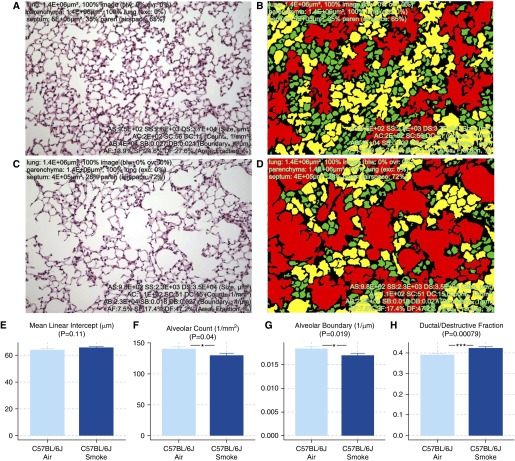
Figure 4.
Comparison of mean linear intercept (MLI) and parameters quantified with PAP. (A–D) Healthy (A) and emphysematous (C) mouse lungs were subjected to double-distribution categorization, color coding, and quantification (B and D). Three distinct subpopulations of airspaces corresponding to single alveolus, alveolar sac, and ductal/destructive airspace were colored green, yellow, and red, respectively. (E–H) Parameters generated from PAP, such as alveolar count (AC), alveolar boundary (AB), and ductal/destructive fraction (DF), exhibited improved sensitivity compared with MLI. Between smoke- and air-exposed mice: MLI, P = 0.11 (E); AC, P = 0.04 (F); AB, P = 0.019 (G); DF, P = 0.00079 (H). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.