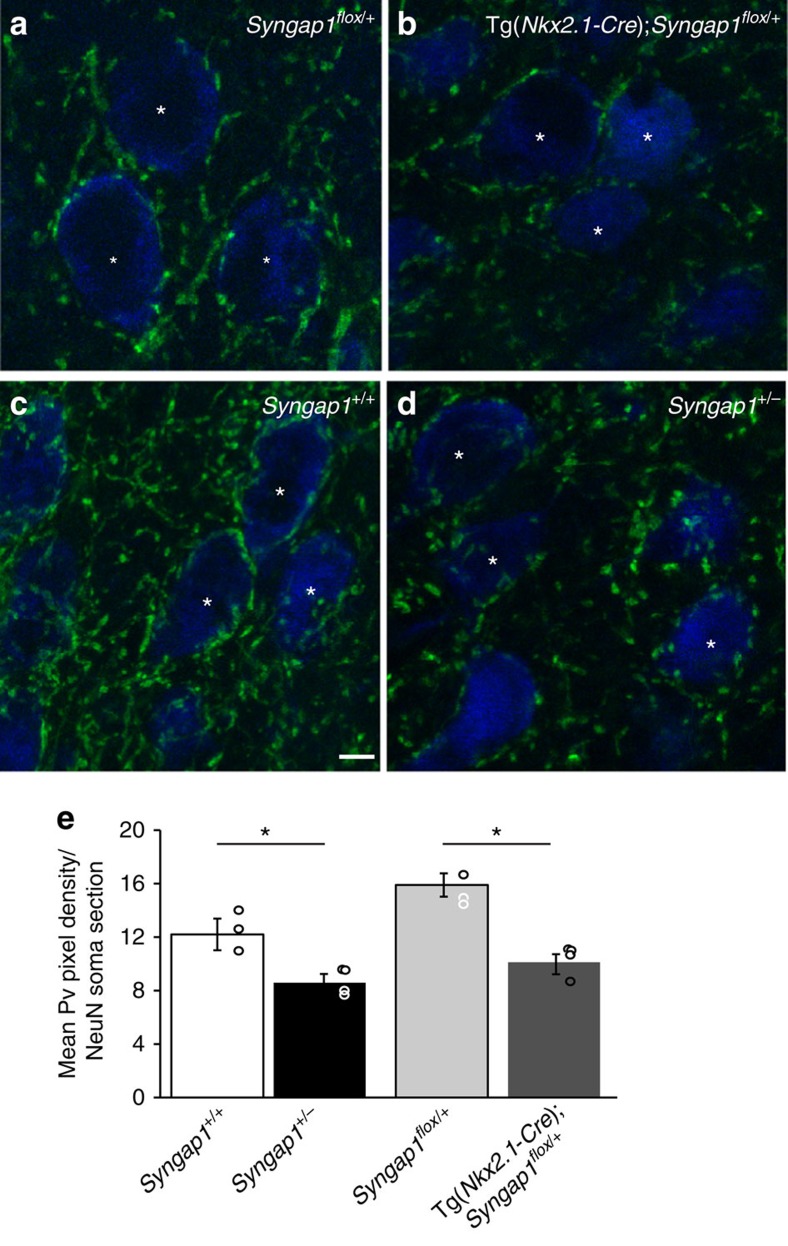
Figure 2. Both MGE-specific and germ-line Syngap1 haploinsufficiency reduce PV+ perisomatic innervation in the cortex of young adult mice.
(a,b) Confocal images of layer 5 pyramidal cells in somatosensory cortex of P45 mice show distinct and intense PV-positive perisomatic rings (green), which enclosed a large portion of neuronal somata (NeuN, blue) in control Syngap1flox/+ mice (a), whereas in Tg(Nkx2.1-Cre);Syngap1flox/+ mice (b) perisomatic PV-ring are less intense and often do not form a complete ring around cell somata. (c,d) Similar differences can be observed between Syngap1+/+(c) and Syngap1+/− (d) mice. (e) Quantification show that mean PV fluorescence per NeuN soma section is significantly reduced in Tg(Nkx2.1-Cre);Syngap1flox/+ and Syngap1+/− compared with their respective control littermates (One-way ANOVA with Dunn's multiple comparisons post hoc method, *P=0.00404 for Tg(Nkx2.1-Cre);Syngap1flox/+ versus Syngap1flox/+, *P=0.0274 versus Syngap1+/− for Syngap1+/+). Graph bars represent mean±s.e.m., circles represent values for each analyzed mouse. n=91 neurons from 3 Syngap1flox/+ mice; n=93 neurons from 4 Tg(Nkx2.1-Cre);Syngap1flox/+ mice, n=100 neurons from 4 Syngap1+/+, n=109 neurons from 4 Syngap1+/−. Scale bar, 10 μm.